A disclaimer of opinion would be issued when the auditor is unable to obtain adequate audit evidence to support management’s assertions in the financial statements. This may result from a scope limitation, such as an inability to obtain evidence about a recorded uncertainty.
Q. Do you have to be a CPA to prepare financial statements?
Only a CPA can prepare an audited financial statement or a reviewed financial statement, although any accountant can prepare a compiled financial statement. While most small businesses may never require an audited or reviewed financial statement, public companies must produce audited statements.
Table of Contents
- Q. Do you have to be a CPA to prepare financial statements?
- Q. Under which of the following circumstances would a disclaimer of opinion on the financial statements of a public company not be appropriate?
- Q. What is an auditor’s responsibility for supplementary information which is outside the basic financial statements but required by the FASB?
- Q. Under which of the following circumstances would an unqualified audit opinion followed by an explanatory paragraph not be appropriate?
- Q. What four circumstances are required for a standard unqualified report?
- Q. Under which of the following circumstances would the expression of a disclaimer?
- Q. Which of the following conditions must be met to issue an unmodified opinion audit report?
- Q. What conditions will affect the auditor’s determination of materiality?
- Q. Which transaction related audit objective has been violated if the acquisition had been capitalized as a fixed asset rather than expensed?
- Q. Is it a must that the auditor not leave questions exceptions in the audit documentation without an sufficient explanation?
- Q. How does a qualified opinion by an auditor differ from an unqualified opinion or an adverse opinion?
- Q. How do you know if an audit is qualified or unqualified?
Q. Under which of the following circumstances would a disclaimer of opinion on the financial statements of a public company not be appropriate?
Under which of the following circumstances would a disclaimer of opinion on the entity’s financial statements not be appropriate? The financial statements fail to contain adequate disclosure of related-party transactions.
Q. What is an auditor’s responsibility for supplementary information which is outside the basic financial statements but required by the FASB?
Question 8 10 / 10 pts (TCO E) (CPA-03186.B) What is an auditor’s responsibility for supplementary information that is outside the basic financial statements but required by the FASB? The auditor has no responsibility for required supplementary information as long as it is outside the basic financial statements.
Q. Under which of the following circumstances would an unqualified audit opinion followed by an explanatory paragraph not be appropriate?
Under which of the following circumstances would an unqualified audit opinion, followed by an explanatory paragraph, not be appropriate? financial statements. The auditor believes that substantial doubt exists concerning the ability of the client to continue as a going concern.
Q. What four circumstances are required for a standard unqualified report?
5. The four circumstances that are required for a standard unmodified opinion audit report to be issued are: 1. All statements—balance sheet, income statement, statement of retained earnings, and statement of cash flows—are included in the financial statements.
Q. Under which of the following circumstances would the expression of a disclaimer?
Under which of the following circumstances would the expression of a disclaimer of opinion be inappropriate? The company issues financial statements that purport to present financial position and results of operations, but refuses to include the related statement of cash flows.
Q. Which of the following conditions must be met to issue an unmodified opinion audit report?
The four conditions that justify issuing a standard unmodified report are: All statements-balance sheet, income statement, statement of changes in stockholder’s equity, and statement of cash flows-are included in the financial statements.
Q. What conditions will affect the auditor’s determination of materiality?
What conditions will affect the auditor’s determination of materiality? (1) dollar amounts compared with a base, (2) effect on potential users of the financial statements, (3) nature of the item. Explain how materiality differs for failure to follow GAAP and for lack of independence.
Q. Which transaction related audit objective has been violated if the acquisition had been capitalized as a fixed asset rather than expensed?
Repair is capitalized as a fixed asset instead of an expense would be violating timing and classification, which is a transaction-related audit objective violation.
Q. Is it a must that the auditor not leave questions exceptions in the audit documentation without an sufficient explanation?
why is it essential that the auditor not leave questions or exceptions in the audit documentation without an adequate explanation? Unanswered questions and exceptions may indicate the potential for significant errors or fraud in the financial statements.
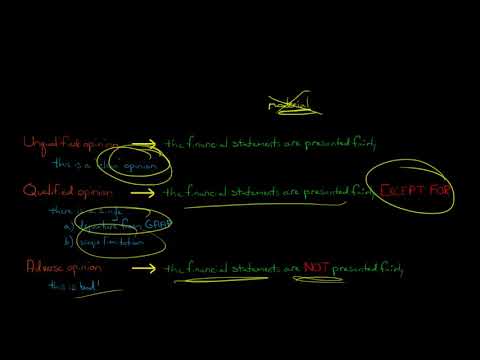
Q. How does a qualified opinion by an auditor differ from an unqualified opinion or an adverse opinion?
A qualified opinion is a reflection of the auditor’s inability to give an unqualified, or clean, audit opinion. An unqualified opinion is issued if the financial statements are presumed to be free from material misstatements.
Q. How do you know if an audit is qualified or unqualified?
2. Opinion on true and fair view of financial statements
- A qualified audit report gives a subjective clearance to the financial statements representing a true and fair view.
- An unqualified audit report opines that the financial statements represent a true and fair view without any limitations.