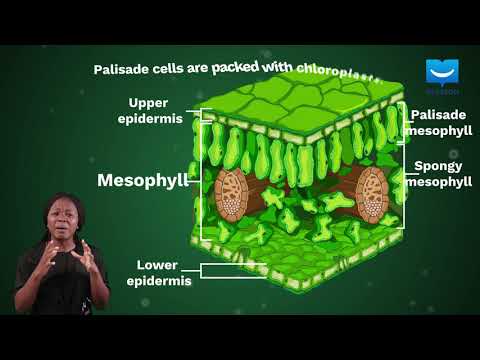
Q. Which part of a plant is adapted for photosynthesis?
leaf
Q. Where is photosynthesis carried out?
chloroplasts
Table of Contents
- Q. Which part of a plant is adapted for photosynthesis?
- Q. Where is photosynthesis carried out?
- Q. What cells carry out photosynthesis?
- Q. Where is the most photosynthesis take place?
- Q. What happens if a plant does not get oxygen?
- Q. What happens to glucose in a plant?
- Q. What are the three uses of glucose in a plant?
- Q. Why is plant glucose important?
- Q. What are the similarities between how plants and humans use glucose?
- Q. How does glucose affect plant growth?
- Q. How do plant cells get glucose?
- Q. What organelles do plant cells have that animal cells do not?
- Q. What are the two types of adaptations that plants can show?
- Q. What is the formula of glucose?
- Q. What is normal blood sugar by age?
- Q. Is glucose a mixture?
- Q. What is the basic structure of glucose?
- Q. Does glucose dissolve in water?
- Q. Is glucose a element?
- Q. What is the structure of ribose sugar?
- Q. Is ribose reducing sugar?
- Q. How do you classify a ribose?
- Q. Which sugar is found in DNA?
- Q. Which sugar is present in a DNA backbone?
- Q. Why is DNA sugar called deoxyribose?
- Q. Where is the nitrogenous base in DNA?
- Q. What does the A stand for in DNA?
- Q. What are the nitrogenous base pairs in DNA?
- Q. What is the location of DNA in a cell?
Q. What cells carry out photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis in plants takes place in specialized organelles called chloroplasts. Located in specific plant cells such as leaf cells, chloroplasts appear in most species that use oxygenic photosynthesis, which – as its name implies – releases oxygen.
Q. Where is the most photosynthesis take place?
the oceans
Q. What happens if a plant does not get oxygen?
In the roots of the plant, oxygen must always be present in the surrounding soil/growth medium for respiration. Therefore if there is no oxygen in the roots then the root cells will be unable to produce ATP from respiration and consequently die.
Q. What happens to glucose in a plant?
During photosynthesis, plants trap light energy with their leaves. Plants use the energy of the sun to change water and carbon dioxide into a sugar called glucose. Glucose is used by plants for energy and to make other substances like cellulose and starch. Cellulose is used in building cell walls.
Q. What are the three uses of glucose in a plant?
WHAT DO PLANTS USE GLUCOSE FOR? RESPIRATION, MAKING FRUITS, MAKING CELL WALLS, MAKING PROTEINS, STORED IN SEEDS AND STORED AS STARCH. PLANTS MAKE GLUCOSE IN THEIR LEAVES AND THEY USE SOME OF IT FOR RESPIRATION.
Q. Why is plant glucose important?
Glucose forms the building blocks of complex carbohydrates, such as starch and cellulose in plants. Plants make and store starch and then break it down into glucose when they need energy. Cellulose is an important substance that forms the cell walls of plants and plays a key role in plant structure.
Q. What are the similarities between how plants and humans use glucose?
The two processes are similar in that they both produce energy, albeit in two different forms. They are different in that photosynthesis assembles the glucose molecule, while cellular respiration takes it apart.
Q. How does glucose affect plant growth?
Glucose affects plant growth and induces delay in development of juvenile to vegetative phase. Glucose induces the synthesis of chlorophyll, rubisco and various photo-protective pigments. Glucose alleviates harmful effects of abiotic stress by increasing antioxidant and sugar level.
Q. How do plant cells get glucose?
Plant cells obtain energy through a process called photosynthesis. This process uses solar energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into energy in the form of carbohydrates. It is a two-part process. Secondly, that energy is used to break down carbon dioxide and form glucose, the main energy molecule in plants.
Q. What organelles do plant cells have that animal cells do not?
Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts and other specialized plastids, and a large central vacuole, whereas animal cells do not.
Q. What are the two types of adaptations that plants can show?
Answer: There are two main types of adaptation: physical and behavioral.
Q. What is the formula of glucose?
C₆H₁₂O₆
Q. What is normal blood sugar by age?
Normal blood glucose levels for adults, without diabetes, is 90 to 110 mg/dL. Learn the symptoms of high and low blood sugar here….Normal blood sugar levels for adolescents.
| Normal blood sugar levels for adolescents | |
|---|---|
| Age 6-12 | mg/dL |
| Fasting | 80-180 |
| Before meal | 90-180 |
| 1-2 hours after eating | Up to 140 |
Q. Is glucose a mixture?
Glucose (C6H12O6) is an organic compound composed of the elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. It is a pure substance, not a mixture.
Q. What is the basic structure of glucose?
Glucose is a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group, and is therefore an aldohexose. The glucose molecule can exist in an open-chain (acyclic) as well as ring (cyclic) form. Glucose is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state.
Q. Does glucose dissolve in water?
Water
Q. Is glucose a element?
Glucose is a compound not an element because, glucose is a molecule having the formula C6H12O6 which means it comprises of 6 carbon atoms, 12 hydrogen and 6 oxygen atoms.
Q. What is the structure of ribose sugar?
Ribose is a simple sugar and carbohydrate with molecular formula C5H10O5 and the linear-form composition H−(C=O)−(CHOH)4−H. The naturally-occurring form, d-ribose, is a component of the ribonucleotides from which RNA is built, and so this compound is necessary for coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes.
Q. Is ribose reducing sugar?
All monosaccharides are reducing sugars because they either have an aldehyde group (if they are aldoses) or can tautomerize in solution to form an aldehyde group (if they are ketoses). This includes common monosaccharides like galactose, glucose, glyceraldehyde, fructose, ribose, and xylose.
Q. How do you classify a ribose?
Ribose is an organic compound classified as a monosaccharide, or simple sugar. Ribose is composed of five carbon atoms, ten hydrogen atoms, and five oxygen atoms that have been bonded together. Ribose is a pentose sugar.
Q. Which sugar is found in DNA?
deoxyribose
Q. Which sugar is present in a DNA backbone?
Q. Why is DNA sugar called deoxyribose?
DNA’s sugar, deoxyribose, has five carbon atoms, which are connected to each other to form what looks like a ring. The sugar in DNA is called a deoxyribose because it doesn’t have a hydroxyl group at the 2′ position. Instead it just has a hydrogen.
Q. Where is the nitrogenous base in DNA?
Nitrogenous bases present in the DNA can be grouped into two categories: purines (Adenine (A) and Guanine (G)), and pyrimidine (Cytosine (C) and Thymine (T)). These nitrogenous bases are attached to C1′ of deoxyribose through a glycosidic bond.
Q. What does the A stand for in DNA?
ACGT is an acronym for the four types of bases found in a DNA molecule: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). A DNA molecule consists of two strands wound around each other, with each strand held together by bonds between the bases. Adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine.
Q. What are the nitrogenous base pairs in DNA?
There are four nucleotides, or bases, in DNA: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). These bases form specific pairs (A with T, and G with C).
Q. What is the location of DNA in a cell?
Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus (where it is called nuclear DNA), but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria (where it is called mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA).