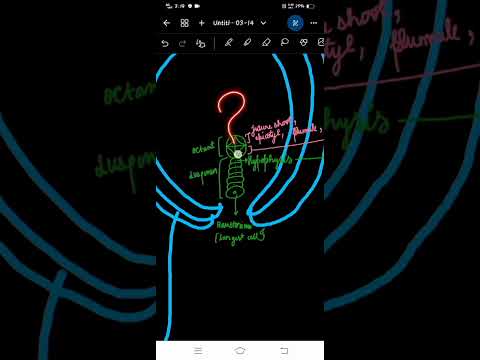
Q. Which part of the plant does the embryo develop?
The plant embryo, sometimes called the seed embryo, is the part of a seed or bud that contains the earliest forms of a plant’s roots, stem and leaves. The embryo develops after a fertilized adult plant flowers, and is generally contained within a seed or bud.
Q. Which part of the seed develops into a new plant?
The plumule is the part of a seed embryo that develops into the shoot bearing the first true leaves of a plant.
Table of Contents
- Q. Which part of the plant does the embryo develop?
- Q. Which part of the seed develops into a new plant?
- Q. What becomes of the embryo when it grows?
- Q. Is a day 6 blastocyst OK?
- Q. Which is better embryo or blastocyst?
- Q. What is the best time for embryo transfer?
- Q. Can you tell gender of blastocyst?
- Q. What is a grade 1 embryo?
- Q. Is a 3AA embryo good?
- Q. Is a BA embryo good?
- Q. Can a Grade 2 embryo implant?
- Q. Is it better to transfer 1 or 2 embryos?
- Q. What is a low grade embryo?
- Q. What are the chances of twins with two embryo transfer?
- Q. Can 1 embryo turn into twins?
- Q. At what stage does an embryo split into twins?
- Q. Can a hatching embryo split into twins?
- Q. What are the signs of having twins?
Q. What becomes of the embryo when it grows?
At the end of embryonic growth, the seed will usually go dormant until germination. Once the embryo begins to germinate (grow out from the seed) and forms its first true leaf, it is called a seedling or plantlet. Plants that produce spores instead of seeds, like bryophytes and ferns, also produce embryos.
Q. Is a day 6 blastocyst OK?
We demonstrated that the blastocysts vitrified on day 6 were of higher quality compared to the blastocyst vitrified on day 5 but still resulted with a significantly lower pregnancy rate. This study is the first to evaluate the pregnancy outcome after transfer of vitrified slow-growing good quality embryos.
Q. Which is better embryo or blastocyst?
Good quality cleavage-stage embryos increases the likelihood of good quality blastocyst embryos. In that study, transfers at blastocyst stage resulted in significantly higher pregnancy (51.3% vs. 27.4%) and live birth (47.5% vs. 27.4%) rates than the transfers at the cleavage stage.
Q. What is the best time for embryo transfer?
Successful embryo implantation requires an embryo free of genetic defects, the proper timing so the embryo is in the uterus during the 8-10 day window of implantation after ovulation, and a uterus optimally ready to receive the embryo.
Q. Can you tell gender of blastocyst?
The sex identification of embryos is done using preimplantation genetic testing (PGT), which involves taking a few cells from an embryo as it develops in the lab, and determining the sex, boy or girl, of the embryos through genetic analysis.
Q. What is a grade 1 embryo?
The embryo grade refers to how the cells in the embryos look. A grade one embryo, for example, is one in which all of the cells are the same size and there is no fragmentation in the embryo.
Q. Is a 3AA embryo good?
Grade ≥ 3AA embryos are considered as the best candidates for SET; however, cases with at least one embryo with grade ≥ 3AA are not frequent [18]. In fact, in our study, 27% of DET cases had an embryo graded greater than 3AA and only 7.6% had two embryos graded 3AA or higher.
Q. Is a BA embryo good?
AB means that the inner cell mass is A and the trophectoderm is B, I’m just going to repeat myself here inner cell mass is what gives rise to the embryo, B is what gives rise to the placenta, so in essence, AB is better than BA because you want the embryo to be a better quality of placenta, however, both these …
Q. Can a Grade 2 embryo implant?
Embryos that are given a poor grade are unlikely to implant after transfer, but other factors are much more important in establishing a pregnancy. A patient’s age for example is the best predictor of pregnancy, regardless of embryo grade. Also there is no correlation between embryo grade and genetic status.
Q. Is it better to transfer 1 or 2 embryos?
1. One is best – most of the time. Research still shows that transferring one embryo per cycle is the safest option. Transferring two increases the chance of a multiple pregnancy and associated complications.
Q. What is a low grade embryo?
Poor quality, or grade C embryos, are defined differently depending on whether it’s a cleavage stage or blastocyst embryo. Poor quality cleavage stage embryos have high fragmentation, poor symmetry or low cell number. Grade C blastocysts (poor quality) have few cells that are loosely packed for the ICM and …
Q. What are the chances of twins with two embryo transfer?
What are my chances of having at least one baby or twins if I transfer two fresh embryos? When two embryos were transferred 2-3 days after retrieval, 49% of women had at least one baby, and 16% had twins. When two embryos were transferred 5-6 days after retrieval, 60% of women had at least one baby, and 27% had twins.
Q. Can 1 embryo turn into twins?
Multiple births can develop through in vitro fertilization when more than one embryo is put back into the mother’s womb. Identical twins can develop even when only one embryo is put back into the womb.
Q. At what stage does an embryo split into twins?
Zygotic splitting occurs between days two and six when the zygote divides, usually into two, and each zygote then goes on to develop into an embryo, leading to identical twins (or triplets if it divides into three). These are known as “monozygotic” twins (or triplets).
Q. Can a hatching embryo split into twins?
There was no evidence of embryo splitting during the hatching – which was one of the theories as to how twins were formed from a single blastocyst. Furthermore, our findings suggest that the formation of two ICMs during blastocyst development may be the cause of the high monozygotic rate after extended culture.
Q. What are the signs of having twins?
Many women who are expecting twins find that they have quite noticeable and very early pregnancy symptoms, including tiredness, emotional ups and downs, nausea, vomiting and constipation. Also, body changes with a twin pregnancy are much more obvious than with a single pregnancy.