Electron
Q. Which object has the most mass?
At the center of this beast is a supermassive black hole — the largest ever seen — with an estimated mass of 20 billion suns.
Table of Contents
- Q. Which object has the most mass?
- Q. Which object has the smallest mass?
- Q. How can you tell if a particle has no charge?
- Q. Which particle has no mass?
- Q. Is a particle with a negative charge?
- Q. What is the smallest charged particle?
- Q. Which subatomic particle has the least mass?
- Q. What is the least massive particle in an atom?
- Q. What are the 3 subatomic particles charges?
- Q. What is the heaviest subatomic particle?
- Q. Which is the lightest particle?
- Q. Which is heavier neutron or positron?
- Q. What is the lightest and heaviest subatomic particle?
- Q. Is most of an atom empty space?
- Q. Why is 99 empty space?
- Q. Are we actually touching things?
- Q. Is there any empty space in the human body?
- Q. Are we made from star dust?
- Q. How old is the matter in my body?
- Q. Are we all made of energy?
Q. Which object has the smallest mass?
Of the three particles, proton, electron, and neutron, which has the smallest mass? The electron exhibits the smallest mass of the three.
Q. How can you tell if a particle has no charge?
Particles with no charge are also contained in the nucleus of the atom. They too have a mass of 1amu. The nucleus has an overall positive charge as it contains the protons. Every atom has no overall charge (neutral).
Q. Which particle has no mass?
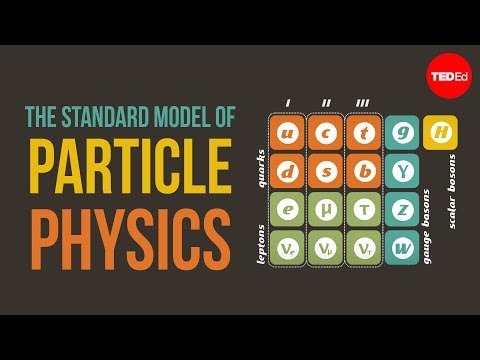
gauge bosons
Q. Is a particle with a negative charge?
Many fundamental, or subatomic, particles of matter have the property of electric charge. For example, electrons have negative charge and protons have positive charge, but neutrons have zero charge.
Q. What is the smallest charged particle?
quarks
Q. Which subatomic particle has the least mass?
electron
Q. What is the least massive particle in an atom?
The majority of an atoms’ mass comes from the protons and neutrons that make up its nucleus. Electrons are the least massive of an atom’s constituent particles, with a mass of 9.11 x 10-31 kg and a size too small to be measured by current techniques.
Q. What are the 3 subatomic particles charges?
Subatomic particles include electrons, the negatively charged, almost massless particles that nevertheless account for most of the size of the atom, and they include the heavier building blocks of the small but very dense nucleus of the atom, the positively charged protons and the electrically neutral neutrons.
Q. What is the heaviest subatomic particle?
Electrons
Q. Which is the lightest particle?
neutrinos
Q. Which is heavier neutron or positron?
So, based on given details we can conclude that neutron is the heaviest subatomic particle amongst proton, neutron, positron and neutron. So, the correct answer is (A) Neutron.
Q. What is the lightest and heaviest subatomic particle?
Electrons are negatively charged and are the heaviest subatomic particle. Protons are positively charged and the lightest subatomic particle. Neutrons have no charge and are the lightest subatomic particle. The mass of a neutron nearly equals the mass of a proton.
Q. Is most of an atom empty space?
Atoms are not mostly empty space because there is no such thing as purely empty space. It’s true that a large percentage of the atom’s mass is concentrated in its tiny nucleus, but that does not imply that the rest of the atom is empty. Rather, it implies that the rest of the atom has relatively low density.
Q. Why is 99 empty space?
Atoms make up everything, but they also exist very, very far apart – and atoms themselves are more void than they are matter. Every atom has a nucleus surrounded by electrons. Every human on planet Earth is made up of millions and millions of atoms which all are 99% empty space.
Q. Are we actually touching things?
The nerve cells that make up our body send signals to our brain that tell us that we are physically touching something. When the touch is merely given to us by our electron’s interaction, the electromagnetic field permeating spacetime (the medium electron waves propagate through).
Q. Is there any empty space in the human body?
Originally Answered: What percentage of your body is empty space? So, the average 70kg human constitutes 7*10^27 atoms, and atoms are very vastly made up of empty space, and therefore the human body is roughly 99.9999999% empty space.
Q. Are we made from star dust?
Planetary scientist and stardust expert Dr Ashley King explains. ‘It is totally 100% true: nearly all the elements in the human body were made in a star and many have come through several supernovas.
Q. How old is the matter in my body?
Every atom in your body is billions of years old. Hydrogen, the most common element in the universe and a major feature of your body, was produced in the big bang 13.7bn years ago.
Q. Are we all made of energy?
Energy. Scientists believe that almost all of your body’s mass comes from the kinetic energy of the quarks and the binding energy of the gluons.