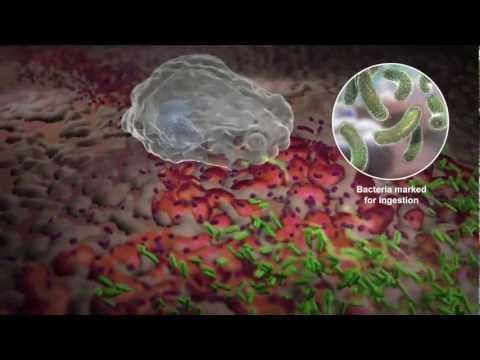
Q. Which process enables a white blood cell to ingest a bacterium quizlet?
Phagocytosis, process by which certain living cells called phagocytes ingest or engulf other cells or particles. The phagocyte may be a free-living one-celled organism, such as an amoeba, or one of the body cells, such as a white blood cell.
Q. When a white blood cell engulfs a bacterium it is using the process of?
A white blood cell engulfs a bacterium through a process called endocytosis.
Table of Contents
- Q. Which process enables a white blood cell to ingest a bacterium quizlet?
- Q. When a white blood cell engulfs a bacterium it is using the process of?
- Q. What is it called when a white blood cell engulfs a bacterium quizlet?
- Q. Which structure helps bacteria cells attach to substrates and aid in exchange of genetic information between cells?
- Q. What are examples of prokaryotes?
- Q. What is it called when bacteria absorb DNA from their environment?
- Q. What are the three types of recombination?
- Q. What type of DNA is bacteria?
- Q. Do bacteria have ER?
- Q. Is bacteria a plant or an animal?
- Q. What does a bacteria cell contain?
- Q. Is virus a cell?
- Q. What is the difference between bacterial cell and human cell?
- Q. Do bacterial cells have Golgi bodies?
- Q. Does bacteria have a cytoplasm?
- Q. What are lysosomes in a cell?
- Q. What does Golgi apparatus do?
- Q. What does Golgi body look like?
- Q. What are the three main functions of the Golgi apparatus?
- Q. Where are Golgi bodies located?
- Q. What is a Golgi body easy definition?
- Q. What color is the Golgi body?
- Q. What Colour is cytoplasm?
- Q. What Colour is a cell wall?
- Q. What color is the plasma membrane in a plant cell?
- Q. What color is a nucleus?
Q. What is it called when a white blood cell engulfs a bacterium quizlet?
White blood cells engulf bacteria through what process? phagocytosis. In receptor-mediated endocytosis, receptor molecules initially project to the outside of the cell.
Q. Which structure helps bacteria cells attach to substrates and aid in exchange of genetic information between cells?
Fimbriae and pili can often be found on the surface of bacterial cells. Fimbriae are short, hair-like projections that attach a bacterium to a substrate or other cells. Pili are similar structures that can serve many functions, including helping the bacterium move or helping it transfer DNA to another bacterium.
Q. What are examples of prokaryotes?
Prokaryotes include the domains, Eubacteria and Archaea. Examples of prokaryotes are bacteria, archaea, and cyanobacteria (blue-green algae).
Q. What is it called when bacteria absorb DNA from their environment?
In transformation, a bacterium takes in DNA from its environment, often DNA that’s been shed by other bacteria. In a laboratory, the DNA may be introduced by scientists (see biotechnology article).
Q. What are the three types of recombination?
There are three types of recombination; Radiative, Defect, and Auger. Auger and Defect recombination dominate in silicon-based solar cells. Among other factors, recombination is associated with the lifetime of the material, and thus of the solar cell.
Q. What type of DNA is bacteria?
Most bacteria have a haploid genome, a single chromosome consisting of a circular, double stranded DNA molecule. However linear chromosomes have been found in Gram-positive Borrelia and Streptomyces spp., and one linear and one circular chromosome is present in the Gram-negative bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
Q. Do bacteria have ER?
No, bacteria do not have endoplasmic reticulum because bacteria is a prokaryotic organism that lacks member bound organelles such as the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi apparatus, etc.
Q. Is bacteria a plant or an animal?
Bacteria are neither animals nor plants.
Q. What does a bacteria cell contain?
It is a gel-like matrix composed of water, enzymes, nutrients, wastes, and gases and contains cell structures such as ribosomes, a chromosome, and plasmids. The cell envelope encases the cytoplasm and all its components. Unlike the eukaryotic (true) cells, bacteria do not have a membrane enclosed nucleus.
Q. Is virus a cell?
Viruses are not made out of cells. A single virus particle is known as a virion, and is made up of a set of genes bundled within a protective protein shell called a capsid.
Q. What is the difference between bacterial cell and human cell?
Short story: Human cells are eukaryotic which means they are more complicated, bacteria cells are prokaryotic which means they are simpler and viruses are not even cells at all, they are just genetic material in a protein shell.
Q. Do bacterial cells have Golgi bodies?
no membrane bound organelles- but there are numerous inclusions and granules. Numerous small ribosomes in cytoplasm. many membrane bound organelles- lysosomes, mitochondria (with small ribosomes), golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleus.
Q. Does bacteria have a cytoplasm?
Bacteria are like eukaryotic cells in that they have cytoplasm, ribosomes, and a plasma membrane.
Q. What are lysosomes in a cell?
Lysosomes are membrane-enclosed organelles that contain an array of enzymes capable of breaking down all types of biological polymers—proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids.
Q. What does Golgi apparatus do?
The Golgi apparatus transports and modifies proteins in eukaryotic cells. How have scientists studied dynamic protein movements through the Golgi? The Golgi apparatus is the central organelle mediating protein and lipid transport within the eukaryotic cell.
Q. What does Golgi body look like?
The Golgi apparatus (GA), also called Golgi body or Golgi complex and found universally in both plant and animal cells, is typically comprised of a series of five to eight cup-shaped, membrane-covered sacs called cisternae that look something like a stack of deflated balloons.
Q. What are the three main functions of the Golgi apparatus?
A major function is the modifying, sorting and packaging of proteins for secretion. It is also involved in the transport of lipids around the cell, and the creation of lysosomes.
Q. Where are Golgi bodies located?
The Golgi is located right near the nucleus. It’s called a perinuclear body, and it’s actually right near the endoplasmic reticulum as well.
Q. What is a Golgi body easy definition?
(GOL-jee BAH-dee) A stack of small flat sacs formed by membranes inside the cell’s cytoplasm (gel-like fluid). The Golgi body prepares proteins and lipid (fat) molecules for use in other places inside and outside the cell. The Golgi body is a cell organelle.
Q. What color is the Golgi body?
pink
Q. What Colour is cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm has no color. Cytoplasm consists of the clear, jelly-like substance that fills the spaces inside a cell, as well as all of the organelles…
Q. What Colour is a cell wall?
dark green
Q. What color is the plasma membrane in a plant cell?
clear
Q. What color is a nucleus?
Animal Cell Coloring
| Cell Membrane (light brown) | Nucleolus (black) | Mitochondria (orange) |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleoplasm (pink) | Cilia (yellow) | Microtubules (green) |
| Nuclear Membrane(dark brown) | Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (dark blue) | Chromosomes (dark green) |
| Ribosome (red) | Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum( light blue) | |