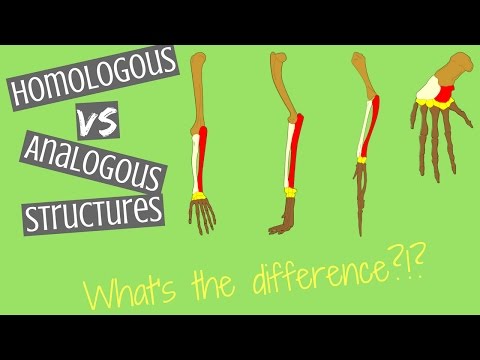
Q. Which structures have the same function but different structure?
Analogous structures are structures which perform the same function, but have different ancestry. 3. We know that organisms must have evolved structures independently if they do not have a common ancestor.
Q. Is a feature that is similar in structure in different organisms but has different function?
Features of animals that have similar structure are classified as homologous if they have a common evolutionary origin, even if they have different functions in different animals. A classic example of homologous structures is that of the wing of a bat and the arm of a human.
Table of Contents
- Q. Which structures have the same function but different structure?
- Q. Is a feature that is similar in structure in different organisms but has different function?
- Q. What are analogous structures?
- Q. When structures share similar function but have evolved on different paths they are said to be?
- Q. What are examples of analogous structures?
- Q. What type of evolution is homologous structures?
- Q. What are 4 types of evidence that support evolution?
- Q. What are the 5 evidences of evolution?
- Q. What are the 3 types of evolution?
- Q. What are the 7 patterns of evolution?
- Q. What does evolved mean?
- Q. What is a good example of evolution?
- Q. What are three examples of natural selection?
- Q. Is evolution still occuring?
- Q. What was the very first animal on earth?
- Q. Is bacteria the oldest organism on earth?
- Q. What was the first animal to be extinct?
- Q. What is the first animal in the Bible?
- Q. What animal is not mentioned in the Bible?
- Q. What animal is mentioned most in the Bible?
- Q. What animal represents the Holy Spirit?
- Q. Does the Bible mention animals?
Q. What are analogous structures?
Alternative Title: analogous structure. Analogy, in biology, similarity of function and superficial resemblance of structures that have different origins. For example, the wings of a fly, a moth, and a bird are analogous because they developed independently as adaptations to a common function—flying.
Q. When structures share similar function but have evolved on different paths they are said to be?
When two or more organs or structures are basically similar to each other in construction but are modified to perform different functions, they are said to be serially homologous.
Q. What are examples of analogous structures?
Examples of analogous structures range from wings in flying animals like bats, birds, and insects, to fins in animals like penguins and fish. Plants and other organisms can also demonstrate analogous structures, such as sweet potatoes and potatoes, which have the same function of food storage.
Q. What type of evolution is homologous structures?
Similar body parts may be homologous structures or analogous structures. Both provide evidence for evolution. Homologous structures are structures that are similar in related organisms because they were inherited from a common ancestor. These structures may or may not have the same function in the descendants.
Q. What are 4 types of evidence that support evolution?
Evidence for evolution: anatomy, molecular biology, biogeography, fossils, & direct observation.
Q. What are the 5 evidences of evolution?
There are five lines of evidence that support evolution: the fossil record, biogeography, comparative anatomy, comparative embryology, and molecular biology.
Q. What are the 3 types of evolution?
shows the three main types of evolution: divergent, convergent, and parallel evolution.
Q. What are the 7 patterns of evolution?
Groups of species undergo various kinds of natural selection and, over time, may engage in several patterns of evolution: convergent evolution, divergent evolution, parallel evolution, and coevolution.
Q. What does evolved mean?
: to change or develop slowly often into a better, more complex, or more advanced state : to develop by a process of evolution.
Q. What is a good example of evolution?
Deer Mouse. Deer mice used to be dark-colored when they primarily lived in the woods. However, a portion of the population split away several thousand years ago and found a new habitat in the sandhills. These deer mice are lighter, having evolved over thousands of years to match their surroundings.
Q. What are three examples of natural selection?
- Deer Mouse.
- Warrior Ants.
- Peacocks.
- Galapagos Finches.
- Pesticide-resistant Insects.
- Rat Snake. All rat snakes have similar diets, are excellent climbers and kill by constriction.
- Peppered Moth. Many times a species is forced to make changes as a direct result of human progress.
- 10 Examples of Natural Selection. « previous.
Q. Is evolution still occuring?
Even with no selection pressures, experts say evolution still occurs by other mechanisms. Professor Stanley Ambrose, an anthropologist from the University of Illinois, explains that “any change in the proportions of genes or gene variants over time is also considered evolution.
Q. What was the very first animal on earth?
comb jelly
Q. Is bacteria the oldest organism on earth?
Permian Bacteria In late 2000, scientists reported that they had revived four unknown strains of bacteria from the Permian era, about 250 million years ago. These Permian bacteria are now considered the oldest living organisms ever discovered in the world.
Q. What was the first animal to be extinct?
With their penchant for hunting, habitat destruction and the release of invasive species, humans undid millions of years of evolution, and swiftly removed this bird from the face of the Earth. Since then, the dodo has nestled itself in our conscience as the first prominent example of human-driven extinction.
Q. What is the first animal in the Bible?
Continuing in chapter 2, the first animal Adam names is ‘cattle’: {2:20} And Adam gave names to all cattle, and to the fowl of the air, and to every beast of the field; but for Adam there was not found an help meet for him. This doesn’t say that Adam encountered ‘cattle’ first, just that he named it first.
Q. What animal is not mentioned in the Bible?
The animals mentioned were important for worship (those suitable for sacrifices) or politically (horses to pull chariots, camels for trade) or symbolic of something (ostriches lacking sense, dogs being despised, snakes being dangerous/cunning). Dogs weren’t mentioned in the bible either.
Q. What animal is mentioned most in the Bible?
dove
Q. What animal represents the Holy Spirit?
The dove
Q. Does the Bible mention animals?
In Genesis 9:3-4 God tells us that a person cannot cut off the limb of a living animal. In Exodus, the Ten Commandments reminds us that we are supposed to treat animals with respect and care, particularly those who work our lands.