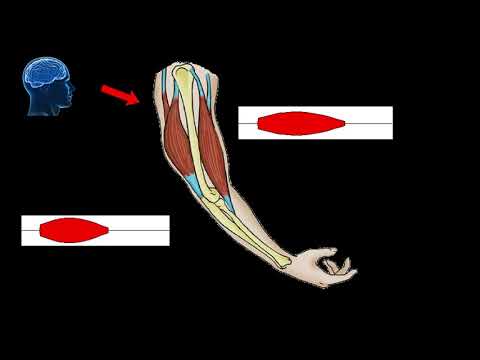
Q. Which system sends signals that make skeletal muscles move?
Skeletal muscles are attached to bones and produce movement at the joints. They are innervated by efferent motor nerves and sometimes by efferent sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves. Every movement of the body has to be correct for force, speed, and position.
Q. How does skeletal muscle produce movement?
Skeletal Muscle Systems | Back to Top. Tendons attach many skeletal muscles across joints, allowing muscle contraction to move the bones across the joint. Muscles generally work in pairs to produce movement: when one muscle flexes (or contracts) the other relaxes, a process known as antagonism.
Table of Contents
- Q. Which system sends signals that make skeletal muscles move?
- Q. How does skeletal muscle produce movement?
- Q. What triggers an action potential in skeletal muscle?
- Q. How long is a skeletal muscle action potential?
- Q. What are the 7 steps of an action potential?
- Q. What is the difference between depolarization and repolarization?
- Q. What starts an action potential?
- Q. What is action potential example?
- Q. Which is true of an action potential?
- Q. What opens first in response to a threshold stimulus?
- Q. What are two factors that cause the movement of sodium and potassium ions?
- Q. What is the membrane potential is becoming more positive than the resting membrane potential?
- Q. What cells carry the electrical signals?
- Q. What are the 3 types of nerve cells?
- Q. What body system sends electrical signals to all other body systems?
- Q. What sends electrical signals to the brain?
- Q. How can I improve my brain signal?
- Q. Does the brain use electrical signals?
- Q. How fast do electrical signals travel in the brain?
- Q. Can electricity damage your brain?
- Q. Do electromagnetic pulse affect brain?
Q. What triggers an action potential in skeletal muscle?
A skeletal muscle action potential is generated when the motor endplate potential is sufficient to raise the surrounding sarcolemmal potential above the threshold for activation of the voltage gated Na+ channels that are abundant throughout the sarcolemma.
Q. How long is a skeletal muscle action potential?
approximately 2-5 ms
Q. What are the 7 steps of an action potential?
An action potential has several phases; hypopolarization, depolarization, overshoot, repolarization and hyperpolarization. Hypopolarization is the initial increase of the membrane potential to the value of the threshold potential.
Q. What is the difference between depolarization and repolarization?
Depolarization is caused when positively charged sodium ions rush into a neuron with the opening of voltage-gated sodium channels. Repolarization is caused by the closing of sodium ion channels and the opening of potassium ion channels.
Q. What starts an action potential?
Action potentials are caused when different ions cross the neuron membrane. A stimulus first causes sodium channels to open. Because there are many more sodium ions on the outside, and the inside of the neuron is negative relative to the outside, sodium ions rush into the neuron.
Q. What is action potential example?
The most famous example of action potentials are found as nerve impulses in nerve fibers to muscles. Neurons, or nerve cells, are stimulated when the polarity across their plasma membrane changes. The polarity change, called an action potential, travels along the neuron until it reaches the end of the neuron.
Q. Which is true of an action potential?
Which of the following is TRUE about an action potential? – An action potential involves the activation of sodium channels. – An action potential increases the membrane potential to +30 mV. – An action potential requires depolarization of the membrane to threshold.
Q. What opens first in response to a threshold stimulus?
What opens first in response to a threshold stimulus? Voltage-gated Na+ channels. The activation gates of voltage-gated Na+ channels open, and Na+ diffuses into the cytoplasm.
Q. What are two factors that cause the movement of sodium and potassium ions?
- the charge of the ion.
- the size of the ion.
- how much water the ion attracts and holds around it.
Q. What is the membrane potential is becoming more positive than the resting membrane potential?
depolarized
Q. What cells carry the electrical signals?
Nerve cells generate electrical signals that transmit information. Although neurons are not intrinsically good conductors of electricity, they have evolved elaborate mechanisms for generating electrical signals based on the flow of ions across their plasma membranes.
Q. What are the 3 types of nerve cells?
For the spinal cord though, we can say that there are three types of neurons: sensory, motor, and interneurons.
- Sensory neurons.
- Motor neurons.
- Interneurons.
- Neurons in the brain.
Q. What body system sends electrical signals to all other body systems?
nervous system
Q. What sends electrical signals to the brain?
Computers and brains both need energy. Computers send electrical signals through wires to control devices. (Your brain also sends electrical signals, but it sends them through nerve cells, called neurons. Signals in neurons transfer information to other neurons and control glands, organs, or muscles.
Q. How can I improve my brain signal?
Meditation or Exercise Regular meditation has been shown to increase alpha waves – your relaxation brain waves — and reduce beta waves – the brain waves of active thought and learning. That’s why it’s most commonly recommended for reducing stress.
Q. Does the brain use electrical signals?
Neurons in the human brain receive electrical signals from thousands of other cells, and long neural extensions called dendrites play a critical role in incorporating all of that information so the cells can respond appropriately.
Q. How fast do electrical signals travel in the brain?
In the human context, the signals carried by the large-diameter, myelinated neurons that link the spinal cord to the muscles can travel at speeds ranging from 70-120 meters per second (m/s) (156-270 miles per hour[mph]), while signals traveling along the same paths carried by the small-diameter, unmyelinated fibers of …
Q. Can electricity damage your brain?
The initial jolt of electricity to the body can affect the central nervous system, motor neurons, and other nerves, as well as their control centers in the brain. These areas are damaged, often leading to a permanent impairment after high voltage exposure.
Q. Do electromagnetic pulse affect brain?
Electromagnetic pulses can induce microglial activation and change the levels of inflammatory cytokines [5]. Previous studies found that EMP can cause brain damage by inducing neuronal oxidative stress and apoptosis [6].