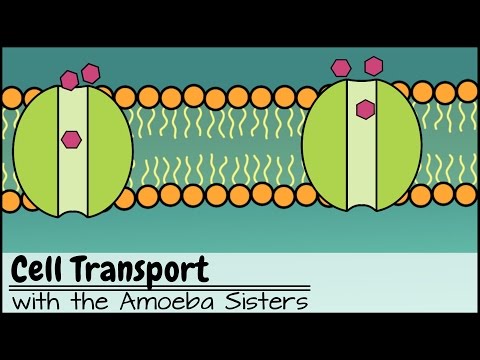
Q. Which transport mechanisms is most probably functioning in the intestinal cells?
The transport mechanism functioning in intestinal cells is facilitated diffusion.
Q. Which transport mechanism is most likely responsible for glucose transport into intestinal cell?
Simple diffusion
Table of Contents
- Q. Which transport mechanisms is most probably functioning in the intestinal cells?
- Q. Which transport mechanism is most likely responsible for glucose transport into intestinal cell?
- Q. How are substances transported across the small intestine?
- Q. What drugs should not be taken with metFORMIN?
- Q. Can I take metformin and vitamins at the same time?
- Q. Can I take vitamin B12 with metformin?
- Q. What vitamins are bad for diabetics?
- Q. What is the best vitamin for diabetes?
- Q. How can type 2 diabetes be cured permanently?
Q. How are substances transported across the small intestine?
Active transport then occurs to allow the plant to take the nutrients it needs for the soil around it. In animals, glucose molecules have to be moved across the gut wall into the blood. At this point it will diffuse from high concentration in the intestine to a lower concentration in the blood.
Q. What drugs should not be taken with metFORMIN?
Other things to avoid while on metformin
- diuretics, such as acetazolamide.
- corticosteroids, such as prednisone.
- blood pressure medication, such as amlodipine (Norvasc)
- anticonvulsants, such as topiramate (Topamax) and zonisamide (Zonegran)
- oral contraceptives.
- antipsychotic drugs, such as chlorpromazine.
Q. Can I take metformin and vitamins at the same time?
People taking metformin should supplement vitamin B12 and folic acid or ask their doctor to monitor folic acid and vitamin B12 levels. The interaction is supported by preliminary, weak, fragmentary, and/or contradictory scientific evidence.
Q. Can I take vitamin B12 with metformin?
No interactions were found between metformin and Vitamin B12.
Q. What vitamins are bad for diabetics?
Supplements that impact blood sugar
- Chromium. A chromium deficiency may lead to high blood sugar levels.
- Vitamin E & St. John’s Wort.
- Niacin. Some people take niacin to raise HDL (“good”) cholesterol, but it can also affect your diabetes management.
Q. What is the best vitamin for diabetes?
Using Supplements for Diabetes Treatment
- Cinnamon.
- Chromium. Chromium is an essential trace element.
- Vitamin B-1. Vitamin B-1 is also known as thiamine.
- Alpha-Lipoic Acid. Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) is a potent antioxidant.
- Bitter Melon.
- Green Tea.
- Resveratrol.
- Magnesium.
Q. How can type 2 diabetes be cured permanently?
Although there’s no cure for type 2 diabetes, studies show it’s possible for some people to reverse it. Through diet changes and weight loss, you may be able to reach and hold normal blood sugar levels without medication. This doesn’t mean you’re completely cured. Type 2 diabetes is an ongoing disease.