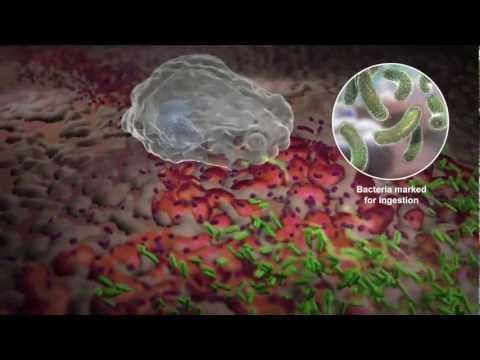
Q. Which transport process occurs in certain white blood cells and macrophages?
Phagocytosis. Phagocytosis (literally, “cell eating”) is a form of endocytosis in which large particles, such as cells or cellular debris, are transported into the cell.
Q. Which vesicular transport process occurs primarily in some white blood cells and macrophages when they engulf a bacterium?
But larger objects, like viruses, bacteria, or other particles are too large to use small channels to transport through the plasma membrane. So, cells engulf the larger objects and pull them in, which is generally called endocytosis. There are many different types of endocytosis, one of which is called phagocytosis.
Table of Contents
- Q. Which transport process occurs in certain white blood cells and macrophages?
- Q. Which vesicular transport process occurs primarily in some white blood cells and macrophages when they engulf a bacterium?
- Q. Which vesicular transport process occurs in some white blood cells?
- Q. Which transport process is the main mechanism for movement of most macromolecules by body cells?
- Q. What are 4 types of active transport?
- Q. What is a real life example of endocytosis?
- Q. What are three examples of diffusion from real life?
- Q. What are two examples of active and passive transport?
- Q. What are 2 examples of passive transport?
- Q. What is the difference between active and passive transport give examples?
- Q. Does passive transport require ATP?
- Q. What is passive transport and examples?
- Q. Does glucose transport require ATP?
- Q. Is glucose transport active or passive?
- Q. Is glucose transported by active transport?
- Q. What type of transport does oxygen use?
- Q. How does glucose get into cells?
- Q. How do cells take in oxygen?
- Q. What occurs at the cellular level when oxygen is not delivered to your body tissue?
- Q. How does oxygen break down glucose?
- Q. Where does oxygen used in cellular respiration end up?
Q. Which vesicular transport process occurs in some white blood cells?
Endocytosis is the process by which cells take in substances from outside of the cell by engulfing them in a vesicle.
Q. Which transport process is the main mechanism for movement of most macromolecules by body cells?
Endocytosis. Endocytosis is a type of active transport that moves particles, such as large molecules, parts of cells, and even whole cells, into a cell.
Q. What are 4 types of active transport?
CONTENTS
- Antiport Pumps.
- Symport Pumps.
- Endocytosis.
- Exocytosis.
Q. What is a real life example of endocytosis?
Endocytosis is a process by which a cell incorporates a big particle, microorganisms or a whole cell inside it. Phagocytosis is an example of endocytosis, by which white blood cells such as neutrophils engulf the microorganisms.
Q. What are three examples of diffusion from real life?
10 Examples Of Diffusion In Everyday Life
- Perfumes/Incense Sticks.
- Helium Balloons.
- Tea Bags.
- Soda/Cold Drinks.
- Breathing.
- Air Pollution.
- Transport Of Minerals and Biomolecules in Plants and Animals.
- Removal of Toxins and Waste Substances from Our Body.
Q. What are two examples of active and passive transport?
Examples of active transport include sodium-potassium pump, uptake of mineral ions by the roots of the plants, etc. Whereas, the examples of passive transport include the exchange of gases in the alveoli of the lungs and the exchange of nutrients in the kidneys.
Q. What are 2 examples of passive transport?
Examples of Passive Transport
- simple diffusion.
- facilitated diffusion.
- filtration.
- osmosis.
Q. What is the difference between active and passive transport give examples?
In Active transport the molecules are moved across the cell membrane, pumping the molecules against the concentration gradient using ATP (energy). In Passive transport, the molecules are moved within and across the cell membrane and thus transporting it through the concentration gradient, without using ATP (energy).
Q. Does passive transport require ATP?
Passive transport is along the gradient and requires no energy, like gas spreading out from a corner of a room. Active transport is against the gradient and requires energy, in this case, in the form of ATP.
Q. What is passive transport and examples?
Summary. Passive transport does not require energy input. An example of passive transport is diffusion, the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Carrier proteins and channel proteins are involved in facilitated diffusion.
Q. Does glucose transport require ATP?
Function/physiology of SGLTs and GLUTs SGLTs do not directly utilize ATP to transport glucose against its concentration gradient; rather, they must rely on the sodium concentration gradient generated by the sodium–potassium ATPase as a source of chemical potential.
Q. Is glucose transport active or passive?
The glucose carriers are passive transporters that have a binding site for glucose that alternates between being accessible to one side of a membrane versus the other side, a mechanism that can be imagined as two bananas rocking back and forth.
Q. Is glucose transported by active transport?
Here, the cell can’t import glucose for free using diffusion, because the natural tendency of the glucose will be to diffuse out rather than flowing in. Instead, the cell must bring in more glucose molecules via active transport.
Q. What type of transport does oxygen use?
The transport of oxygen is fundamental to aerobic respiration. Oxygen transport within the human body occurs through both convection and diffusion. Within the pulmonary capillaries, one haemoglobin molecule binds up to four oxygen molecules in a cooperative manner.
Q. How does glucose get into cells?
Cells obtain energy from glucose or convert it to fat for long-term storage. Like a key fits into a lock, insulin binds to receptors on the cell’s surface, causing GLUT4 molecules to come to the cell’s surface. As their name implies, glucose transporter proteins act as vehicles to ferry glucose inside the cell.
Q. How do cells take in oxygen?
The oxygen enters the bloodstream from the alveoli, tiny sacs in the lungs where gas exchange takes place (Figure below). The transfer of oxygen into the blood is through simple diffusion. The oxygen molecules move, by diffusion, out of the capillaries and into the body cells.
Q. What occurs at the cellular level when oxygen is not delivered to your body tissue?
The consequence of oxygen deprivation in tissues is a switch to anaerobic metabolism at the cellular level. As such, reduced systemic blood flow may result in increased serum lactate.
Q. How does oxygen break down glucose?
Aerobic respiration Glucose is oxidised to release its energy, which is then stored in ATP molecules. Aerobic respiration breaks down glucose and combines the broken down products with oxygen, making water and carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide is a waste product of aerobic respiration because cells do not need it.
Q. Where does oxygen used in cellular respiration end up?
electron transport chain