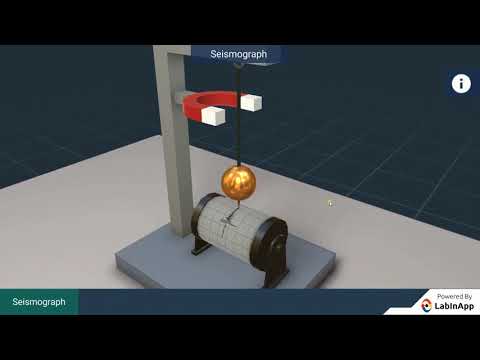
How Are Earthquakes Studied? Seismologists study earthquakes by going out and looking at the damage caused by the earthquakes and by using seismographs. A seismograph is an instrument that records the shaking of the earth’s surface caused by seismic waves.
Q. What information about earthquakes is gathered from seismographs?
A seismograph, or seismometer, is an instrument used to detect and record earthquakes. Generally, it consists of a mass attached to a fixed base. During an earthquake, the base moves and the mass does not. The motion of the base with respect to the mass is commonly transformed into an electrical voltage.
Table of Contents
- Q. What information about earthquakes is gathered from seismographs?
- Q. What information can be obtained from the seismogram?
- Q. How does a seismometer detect earthquakes?
- Q. What is the atomic bomb equivalent to a 7.0 earthquake?
- Q. How do you know when earthquake is coming?
- Q. Do small earthquakes mean a big one is coming?
- Q. Does an earthquake make a sound?
- Q. Can you sense an earthquake before it happens?
- Q. Can dogs sense an earthquake coming?
- Q. Where is the safest place to be during an earthquake?
- Q. Is it safe to go under the bed during an earthquake?
- Q. Where do 90% of earthquakes occur?
- Q. In which country there is no earthquake?
- Q. Where do most earthquakes occur on Earth?
- Q. Where does an earthquake start?
- Q. Which country has the most earthquakes in Europe?
- Q. What country has the worst earthquakes?
- Q. When was the last earthquake in Europe?
- Q. Which country has the most tsunamis?
- Q. When was the last tsunami in the world?
Q. What information can be obtained from the seismogram?
Seismograms are used to determine the location and magnitude of earthquakes. An earthquake’s magnitude may be considered to vary as a function of the amount of energy released at the rupture point.
Q. How does a seismometer detect earthquakes?
Measuring Magnitude Modern seismometers record ground motions using electronic motion detectors. The data are then kept digitally on a computer. These seismograms show the arrival of P-waves and S-waves. The surface waves arrive just after the S-waves and are difficult to distinguish.
Q. What is the atomic bomb equivalent to a 7.0 earthquake?
More examples
| Approximate Richter Magnitude number | Seismic energy equivalent: Amount of TNT |
|---|---|
| 7.0 | 32 megatons |
| 7.1 | 50 megatons |
| 7.5 | 178 megatons |
| 7.8 | 600 megatons |
Q. How do you know when earthquake is coming?
Though there is no way to pinpoint the exact arrival of an earthquake, scientists can examine sediment samples to get an idea of when major earthquakes occurred in the past. By measuring the amount of time between events, they can come up with a rough idea of when a major quake might hit.
Q. Do small earthquakes mean a big one is coming?
“Every time a small earthquake happens, doesn’t mean there is going to be a larger one,” according to Chung.
Q. Does an earthquake make a sound?
Small shallow earthquakes sometimes produce rumbling sounds or booms that can be heard by people who are very close to them. High-frequency vibrations from the shallow earthquake generate the booming sound; when earthquakes are deeper, those vibrations never reach the surface.
Q. Can you sense an earthquake before it happens?
No. Neither the USGS nor any other scientists have ever predicted a major earthquake. We do not know how, and we do not expect to know how any time in the foreseeable future. USGS scientists can only calculate the probability that a significant earthquake will occur in a specific area within a certain number of years.
Q. Can dogs sense an earthquake coming?
But wait—how would a dog know an earthquake is coming? Dogs have a wider hearing range and better scent detection than humans. Some scientists suggest that dogs can hear seismic activities that precede earthquakes (such as the scraping, grinding, and breaking of rocks underground).
Q. Where is the safest place to be during an earthquake?
COVER your head and neck (and your entire body if possible) underneath a sturdy table or desk. If there is no shelter nearby, get down near an interior wall or next to low-lying furniture that won’t fall on you, and cover your head and neck with your arms and hands.
Q. Is it safe to go under the bed during an earthquake?
Don’t hide under the bed If you are in bed during the night and an earthquake occurs, simply roll off the bed. The bed will hold up some of the debris, creating a safe void around the perimeter. Never get under it, and teach your children never to crawl under the bed in an earthquake.
Q. Where do 90% of earthquakes occur?
plate boundaries
Q. In which country there is no earthquake?
Antarctica
Q. Where do most earthquakes occur on Earth?
Pacific Ocean
Q. Where does an earthquake start?
The location below the earth’s surface where the earthquake starts is called the hypocenter, and the location directly above it on the surface of the earth is called the epicenter.
Q. Which country has the most earthquakes in Europe?
The highest earthquake hazard is concentrated in south-eastern areas of Europe, e.g. Greek, Italy and Romania. With the theory of plate tectonics, it has become evident that most earthquakes occur along the margins of plates, where one plate comes into contact with another, developing shear stresses.
Q. What country has the worst earthquakes?
China
Q. When was the last earthquake in Europe?
Latest earthquakes in or near Europe today, past 24 hours, Tuesday, 15 Jun 2021
| Date and time | Mag Depth | Map |
|---|---|---|
| 15 Jun 2021 11:02:31 GMT just now | 2.1 5 km | Map |
| 15 Jun 2021 10:23:42 GMT just now | 2.0 | Map |
| 15 Jun 2021 10:18:19 GMT just now | 2.0 1 km | Map |
| 15 Jun 2021 09:25:28 GMT just now | 2.0 | Map |
Q. Which country has the most tsunamis?
Indonesia
Q. When was the last tsunami in the world?
Jan