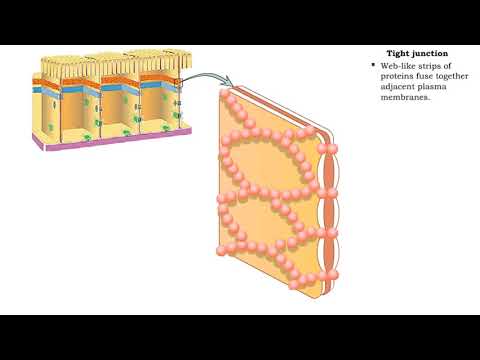
Q. Which type of junctions will create a solid barrier to prevent molecules from moving between the cell?
Tight Junctions: Tight junctions merge cell membranes together to form a strong, impenetrable barrier. When many cells are linked together, they form a wall that does not allow anything located on one side to pass to the other side. In other words, tight junctions allow your body to keep areas separated.
Q. Do plant cells have gap junctions?
Gap junctions in animal cells are like plasmodesmata in plant cells in that they are channels between adjacent cells that allow for the transport of ions, nutrients, and other substances that enable cells to communicate (Figure 5).
Table of Contents
- Q. Which type of junctions will create a solid barrier to prevent molecules from moving between the cell?
- Q. Do plant cells have gap junctions?
- Q. What connects plant cells to each other?
- Q. What are the junctions between cells?
- Q. What cells are tight junctions found in?
- Q. What is the function of plasmodesmata in plant cells?
- Q. Where is Plasmodesmata found in plants?
- Q. Do plant cells have receptors?
- Q. What are the plasmodesmata in plant cells what can pass through them?
- Q. What are the plasmodesmata in plant cells what can pass through them quizlet?
Q. What connects plant cells to each other?
Plasmodesmata (singular, plasmodesma) are small channels that directly connect the cytoplasm of neighboring plant cells to each other, establishing living bridges between cells.
Q. What are the junctions between cells?
Cell junctions (or intercellular bridges) are a class of cellular structures consisting of multiprotein complexes that provide contact or adhesion between neighboring cells or between a cell and the extracellular matrix in animals.
Q. What cells are tight junctions found in?
Tight junctions are located within our body’s epithelia. Epithelia is the plural of epithelium. Epithelium is a word that refers to the covering of the body’s internal and external surfaces. This includes organs (such as skin), blood vessels, and cavities.
Q. What is the function of plasmodesmata in plant cells?
Plasmodesmata (PD) are membrane-lined channels that transverse the plant cell wall and function as conduits to allow the exchange of various cellular molecules between plant cells1.
Q. Where is Plasmodesmata found in plants?
Plasmodesmata (singular form: plasmodesma) are intercellular organelles found only in plant and algal cells. (The animal cell “equivalent” is called the gap junction.) The plasmodesmata consist of pores, or channels, lying between individual plant cells, and connect the symplastic space in the plant.
Q. Do plant cells have receptors?
Like animals, plants make extensive use of cell-surface receptors. Like the animal receptors, however, they have a typical serine/threonine kinase cytoplasmic domain and an extracellular ligand-binding domain.
Q. What are the plasmodesmata in plant cells what can pass through them?
Plasmodesmata: A plasmodesma is a channel between the cell walls of two adjacent plant cells. Plasmodesmata allow materials to pass from the cytoplasm of one plant cell to the cytoplasm of an adjacent cell.
Q. What are the plasmodesmata in plant cells what can pass through them quizlet?
The continuous cytoplasmic space between the plasma and desmotubule membrane, and is thought to be where small molecules (sugars, amino acids, ions) can pass to get from one cell wall to another.