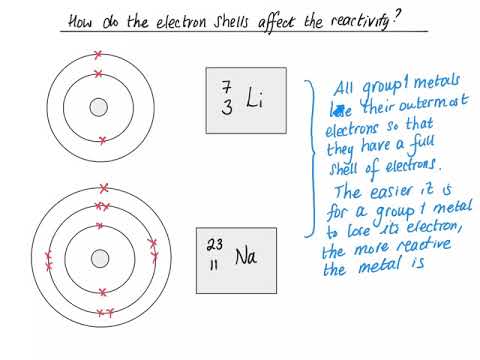
Q. Why are the 1A and 7A elements so reactive?
A group is a vertical column of the periodic table. All of the 1A elements have one valence electron. This is what causes these elements to react in the same ways as the other members of the family.
Q. What are the Group 1A and Group 7A elements?
Several groups of representative elements are known by common names. Group 1A(1), the alkali metals, includes lithium, sodium, and potassium. Group 7A(17) the halogens, includes chlorine, bromine, and iodine.
Table of Contents
- Q. Why are the 1A and 7A elements so reactive?
- Q. What are the Group 1A and Group 7A elements?
- Q. Are groups 1A and 7A stable?
- Q. Why does Group 7A have a 1 charge?
- Q. What is the charge of Group 7A?
- Q. Which group has a 2 charge?
- Q. What element is in Group 5 Period 4?
- Q. Why do boiling points decrease down Group 1?
- Q. Why are boiling points of Group 4 hydrides lower than hydrides of Group 5/6 and 7?
- Q. Why does boiling point increase down Group 6?
- Q. Why does ammonia have a higher boiling point than methane?
- Q. Which attractive force is the weakest?
- Q. Which state of matter has the strongest intermolecular forces?
- Q. Which state of matter has the weakest to strongest intermolecular forces?
- Q. Which bond is available in the three state of matter?
- Q. Which state of matter has the least number of intermolecular forces?
Q. Are groups 1A and 7A stable?
Because the alkali metals are very reactive, they are seldom (if ever) found in their elemental form in nature, and are usually found as ionic compounds (except for hydrogen). The alkali metals have only one valence electron in their highest-energy orbitals (ns1)….Group 1A — The Alkali Metals.
| 4A | (14) |
|---|---|
| 5A | (15) |
| 6A | (16) |
| 7A | (17) |
| 8A | (18) |
Q. Why does Group 7A have a 1 charge?
The Group 7A elements have seven valence electrons in their highest-energy orbitals (ns2np5). This is one electron away from having a full octet of eight electrons, so these elements tend to form anions having -1 charges, known as halides: fluoride, F-; chloride, Cl-, bromide, Br-, and iodide, I-.
Q. What is the charge of Group 7A?
1- charges
Q. Which group has a 2 charge?
alkali earth metals
Q. What element is in Group 5 Period 4?
Group 5A (or VA) of the periodic table are the pnictogens: the nonmetals nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P), the metalloids arsenic (As) and antimony (Sb), and the metal bismuth (Bi).
Q. Why do boiling points decrease down Group 1?
When any of the Group 1 metals is melted, the metallic bond is weakened enough for the atoms to move more freely, and is broken completely when the boiling point is reached. The decrease in melting and boiling points reflects the decrease in the strength of each metallic bond.
Q. Why are boiling points of Group 4 hydrides lower than hydrides of Group 5/6 and 7?
All the group 4 hydrides have a regular tetrahedral shape and are non-polar. The only intermolecular forces between such molecules are weak van der Waals’ forces. These generally increase with increasing relative molecular mass.
Q. Why does boiling point increase down Group 6?
The partial charges, induced by the higher electronegativity of oxygen, mean that the hydrogens and oxygens will be attracted to one another by coloumbic forces. This in turn will increase the energy needed to pull the molecules apart, thus an increase in the boiling point is observed.
Q. Why does ammonia have a higher boiling point than methane?
In case of ammonia, due to the presence of electronegative atom, the bond is sufficiently polar to form intermolecular hydrogen bonding. So, boiling point of ammonia is much greater than methane.
Q. Which attractive force is the weakest?
London dispersion force
Q. Which state of matter has the strongest intermolecular forces?
Solids
Q. Which state of matter has the weakest to strongest intermolecular forces?
The Intermolecular force is strongest in solids and weakest in gases.
Q. Which bond is available in the three state of matter?
The three states of matter are: Solids: The strong bonds between molecules make solids rigid and very difficult to deform. Liquids: The relatively weak bonds between molecules allow liquids to be deformed without effort.
Q. Which state of matter has the least number of intermolecular forces?
gaseous state