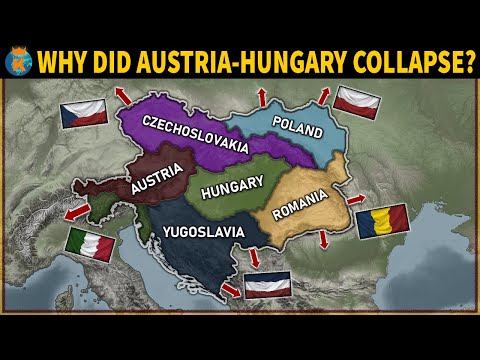
Southern Austria and were keen to unite with Serbia. better to conquer Serbia to stop the threat as the Czechs and Croats also wanted independence. establish pro-Russian governments in the Balkans which would allow their ports to be used to transport Russian goods in the Mediterranean.
Q. Why did Austria-Hungary hate Serbia?
They felt this was inadequate and blamed Austria-Hungary for their loss of land. This was a significant factor in the hostility between the two sides as it made Austria-Hungary fear Serbian growth and angered Serbia as they felt that whenever they made gains of land in the Balkans the Austrians would thwart it.
Table of Contents
- Q. Why did Austria-Hungary hate Serbia?
- Q. Why did Austria-Hungary want Bosnia?
- Q. What was the effect of Austria-Hungary’s annexation of Bosnia?
- Q. Why did Serbia want Bosnia?
- Q. Why were Serbians unhappy in Bosnia?
- Q. Who won Bosnian war?
- Q. What did the Bosnian Serbs want in ww1?
- Q. Are Bosnians Serbs?
- Q. How many Serbians died in Bosnia?
- Q. What’s the difference between Serbians and Croatians?
- Q. What language is closest to Serbian?
- Q. Is Serbia a third world country?
- Q. What religion is in Serbia?
- Q. What religion is Serbian Orthodox?
- Q. What was Serbia called before?
- Q. What is the traditional food of Serbia?
- Q. What is soccer called in Serbia?
- Q. Who is the best team in Serbia?
- Q. What alcohol do Serbians drink?
- Q. What is Serbian Slava?
- Q. What do you speak in Serbia?
- Q. Is Serbia Russian?
- Q. Is Serbia still a country?
Q. Why did Austria-Hungary want Bosnia?
As the provinces were coveted by many—in fact, both Austria and Hungary wanted Bosnia and Herzegovina for themselves—the decision was more or less a stopgap to preserve the delicate balance of power in Europe.
Q. What was the effect of Austria-Hungary’s annexation of Bosnia?
The annexation of Bosnia and Herzegovina by Austria-Hungary in October, 1908, led to a controversy between the Dual Monarchy and Turkey. It also led to international complications which for several weeks early in 1909 threatened to end in a general European war. This was the Bosnian crisis.
Q. Why did Serbia want Bosnia?
To spite Austria-Hungary, Izvolsky then suggested that Serbia should receive territorial compensation from Austria-Hungary to balance up the land annexed from Bosnia-Herzegovina. This Austria refused to even consider. Serbia had been against the annexation, as she wanted Bosnia-Herzegovina for herself.
Q. Why were Serbians unhappy in Bosnia?
Furthermore, Serbia, which was closely related to Bosnia and Herzegovina geographically and ethnically, was outraged by the annexation. It demanded that Austria cede a portion of Bosnia and Herzegovina to Serbia, and Izvolsky, pressed by anti-Austrian opinion in Russia, was forced to support the Serbian claims.
Q. Who won Bosnian war?
The war ended in 1995 after Nato bombed the Bosnian Serbs and Muslim and Croat armies made gains on the ground. A US-brokered peace divided Bosnia into two self-governing entities, a Bosnian Serb republic and a Muslim-Croat federation lightly bound by a central government.
Q. What did the Bosnian Serbs want in ww1?
Inspired by Serbia’s Slobodan Milosevic as he turned from Communism to nationalism, Bosnia’s Serbs set about trying to unite Bosnia with Serbia, in an echo of Princip’s dream.
Q. Are Bosnians Serbs?
Bosnian Serbs are also the largest Serb community outside of Serbia itself. The main dispute in Bosnia arose from the dissolution of Yugoslavia, when most Serbs did not support the country’s independence, but instead joined the Serbian war-effort to dismember Bosnia and attach Serb controlled areas to Serbia.
Q. How many Serbians died in Bosnia?
| Bosnian Genocide | |
|---|---|
| Date | 11 July 1995 – 13 July 1995 |
| Target | Bosniak men and prisoners of war |
| Attack type | mass murder, ethnic cleansing, deportation, etc. |
| Deaths | Genocide: 8,372 killed (Srebrenica) |
Q. What’s the difference between Serbians and Croatians?
Both Croat and Croatian refer to the language and people of Croatia; Serbian refers to the language of Serbia, while Serb designates the people. Serbs and Croats understand one another’s speech, but their alphabets are very different. Lejla’s mother is a Serb, and her father is a Croat, but she is a Canadian.
Q. What language is closest to Serbian?
The closest languages are Croatian, Macedonian, Bulgarian and Slovenian. Russian is kind of close but not so much. There are some main differences in accent (Serbians speak with a hard accent and we generally speak very fast), grammar etc.
Q. Is Serbia a third world country?
The World Bank classifies Serbia as a middle-income country and its economy is transitioning from being dominated by the state sector to a market-driven model. The country is a member of the IMF, United Nations and WHO and is a candidate country for the European Union.
Q. What religion is in Serbia?
Currently, according to the Census in Serbia, in regard to religious affiliation, there are 84.6% Orthodox Christians, 5% Catholics, 3.1% Muslims, 1.1% atheists, 1% Protestants, 3.1% do not declare themselves confessionally, and about 2% other confessions.
Q. What religion is Serbian Orthodox?
Serbian Orthodox Church
| Serbian Orthodox Church Српска православна црква Srpska pravoslavna crkva | |
|---|---|
| Classification | Eastern Orthodox |
| Scripture | Septuagint, New Testament |
| Theology | Eastern Orthodox theology |
| Primate | Porfirije |
Q. What was Serbia called before?
Yugoslavia
Q. What is the traditional food of Serbia?
National dishes of Serbia include sarma (a mix of ground pork or beef with rice rolled in leaves of cabbage), gibanica (an egg and cheese pie made with filo dough), pljeskavica (a ground beef or pork patty), ćevapi (grilled meat), paprikaš (a soup made of fish), gulaš] ( soup of meat and vegetables usually seasoned …
Q. What is soccer called in Serbia?
Red Star Belgrade, byname of Fudbalski Klub Crvena Zvezda (Serbian: “Football Club Red Star”), also known as Red Star, Serbian professional football (soccer) team based in Belgrade.
Q. Who is the best team in Serbia?
By far the two most popular clubs in the country are Partizan and Crvena zvezda, both from Belgrade.
Q. What alcohol do Serbians drink?
Rakija (Serbian Cyrillic: Ракија) is one of the most popular alcoholic drinks in Serbia. It is the national drink of Serbia present for centuries.
Q. What is Serbian Slava?
In Serbia, Orthodox Christian families celebrate an important holiday in honour of the patron saint, Slava, who is believed to be their protector and provider of welfare. The celebration consists of the ritual offering of a bloodless sacrifice and a feast held for relatives, neighbours and friends.
Q. What do you speak in Serbia?
Serbia has only one nationwide official language, which is Serbian. Other languages spoken in Serbia include Hungarian, Romanian, Slovak, Rusyn, Croatian (all of which are official regional languages in the Vojvodina province), Bosnian, Romani, Albanian, Vlach, Bulgarian, Macedonian, Montenegrin, Bunjevac, etc.
Q. Is Serbia Russian?
According to censuses, there were 3,247 ethnic Russians living in Serbia (2011) and 3,510 Serbs with Russian citizenship (2010). Russia and Serbia are both predominantly Slavic and Eastern Orthodox countries, which share a strong mutual cultural affinity.
Q. Is Serbia still a country?
Location: Serbia is a landlocked country in South East Europe which covers part of the Pannonian Plain and Central and Western Balkan Peninsula. It borders Hungary to the north, Romania and Bulgaria to the east, North Macedonia and Kosovo to the south, and Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Montenegro to the west.