(a) Law enforcement vessels may display a flashing blue light when engaged in direct law enforcement or public safety activities. This light must be located so that it does not interfere with the visibility of the vessel’s navigation lights.
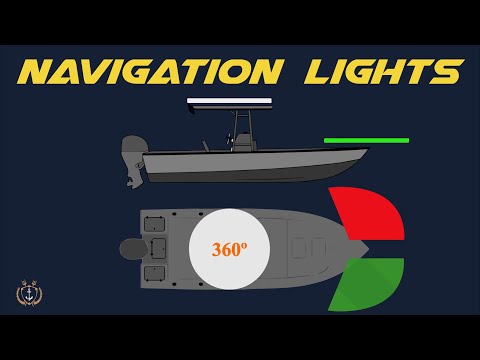
Q. What lights does a trawler display at night?
Commercial fishing vessel trawling Two all-round lights, the top light green and the lower light white. A rear masthead light is optional for fishing vessels under 50 m in length. Making way through water, sidelights and sternlights are shown.
Table of Contents
- Q. What lights does a trawler display at night?
- Q. What are three short blasts of a horn?
- Q. How many masthead lights should a 100m PDV have?
- Q. What rule is the head on situation?
- Q. How many rules are in Colreg?
- Q. What lights does a cargo ship display?
- Q. What color light goes on the front of a boat?
- Q. Who gives way in sailing?
- Q. What are the basic rules of sailing?
- Q. What are the basics of sailing?
- Q. What does Leeward mean in sailing?
- Q. What is sailing against the wind called?
- Q. Why is it called the leeward side?
- Q. Which best describes the leeward side?
- Q. What does Leeward mean?
- Q. What is the meaning of rainshadow?
- Q. What is the advantage of staying in the leeward side of the mountain?
- Q. Which side of a mountain is colder?
- Q. Which side of the mountain receives the most precipitation?
- Q. What happens on the leeward side of a mountain?
- Q. Is Leeward left or right?
- Q. Which is colder windward or leeward?
- Q. Which side of the mountain is more often cloudy and which side is more often clear?
Q. What are three short blasts of a horn?
One prolonged blast indicates you are getting under way, and three short blasts indicate you are backing up. This is what is sounded when you are departing a dock in reverse. Five Short Blasts – This is the DANGER signal.
Q. How many masthead lights should a 100m PDV have?
two masthead lights
Q. What rule is the head on situation?
a. When two power-driven vessels are meeting on reciprocal or nearly reciprocal courses so as to involve risk of collision each shall alter her course to starboard so that each shall pass on the port side of the other.
Q. How many rules are in Colreg?
41 rules
Q. What lights does a cargo ship display?
What type of boat requires navigation lights?
- masthead light (white) forward,
- sidelights (red – green) and,
- sternlight (white).
Q. What color light goes on the front of a boat?
A masthead light is a white light at the front of the boat. The masthead light needs to be visible across 225 degrees and from two miles away. A stern light, which is a white light at the rear of the boat. The stern light needs to be visible across 135 degrees and from two miles away.
Q. Who gives way in sailing?
When sailboats approach on different tacks the boat on the starboard is the stand on vessel with right of way. The boat on the port tack is the give way vessel and should pass behind the other sailing vessel.
Q. What are the basic rules of sailing?
There are general rules that every sailor should keep in mind:
- Always sail with common sense, safety, and good sportsmanship.
- Right-of-way is not excuse to cause a collision.
- A sailboat in motion shall keep clear of a stopped yacht.
- After finishing your race, keep clear of the course and of other boats still racing.
Q. What are the basics of sailing?
Very simply, the forces of the wind on the sails (aerodynamics) and the water on the underwater parts of the boat (hydrodynamics) combine to propel the boat through the water. The wind blows across the sails, creating aerodynamic lift, like an airplane wing. The lift contains a sideways force and a small forward force.
Q. What does Leeward mean in sailing?
Did you know? In sailing terminology, windward means “upwind,” or the direction from which the wind is blowing. An island’s windward side faces the prevailing, or trade, winds, whereas the island’s leeward side faces away from the wind, sheltered from prevailing winds by hills and mountains.
Q. What is sailing against the wind called?
Sailing Upwind As you steer more toward the wind direction, you trim the sails in tighter to keep them full, and keep generating lift. But sail too close to the wind and the sail will “luff”— the forward edge will start to flutter in and out and the boat will slow down.
Q. Why is it called the leeward side?
The leeward side is the side protected by the elevation of the island from the prevailing wind, and is typically the drier side of an island. Thus, leeward or windward siting is an important weather and climate factor on oceanic islands.
Q. Which best describes the leeward side?
The adjective leeward describes an area or side of a boat that’s facing away from the wind. If you move to the leeward side of your sailboat, you’re shifting to the sheltered, downwind side. You’re likely to hear the word leeward when you’re on a boat, since wind direction is hugely important when you’re sailing.
Q. What does Leeward mean?
: being in or facing the direction toward which the wind is blowing also : being the side opposite the windward. Synonyms & Antonyms Example Sentences Learn More about leeward.
Q. What is the meaning of rainshadow?
A rain shadow is a patch of land that has been forced to become a desert because mountain ranges blocked all plant-growing, rainy weather. On one side of the mountain, wet weather systems drop rain and snow. On the other side of the mountain—the rain shadow side—all that precipitation is blocked.
Q. What is the advantage of staying in the leeward side of the mountain?
Leeward Mountain Slopes Encourage Warm, Dry Climates Opposite from the windward side is the lee side—the side sheltered from the prevailing wind. This is often the eastern side of the mountain range because prevailing winds in the mid-latitudes blow from the west, but that is not necessarily always the case.
Q. Which side of a mountain is colder?
As the air moves up the windward side of a mountain, it cools, and the volume decreases. As a result, humidity increases and orographic clouds and precipitation can develop. When the air descends the leeward side, it warms and is drier because the moisture in the air was wrung out during the ascent.
Q. Which side of the mountain receives the most precipitation?
Much of airborne moisture falls as rain on the windward side of mountains. This often means that the land on the other side of the mountain (the leeward side) gets far less rain—an effect called a “rain shadow”—which often produces a desert.
Q. What happens on the leeward side of a mountain?
The leeward side of a mountain is often associated with warm, dry air. Rain shadows are created on the leeward slopes of mountain ranges, resulting in deserts or other climates characterized by low precipitation. This impacts the condensation water cycle step and the precipitation water cycle step as well.
Q. Is Leeward left or right?
The leeward side is the left side and windward is the right side. The leeward side of the boat is the side opposite the wind. The direction to which the wind is going.
Q. Which is colder windward or leeward?
In meteorology, the study of earth’s atmosphere, there are two sides to any island—the windward side and the leeward side. This is the colder, wetter side of an island.
Q. Which side of the mountain is more often cloudy and which side is more often clear?
The Windward side of the mountain is more often cloudy, while the leetward side is more often clear.