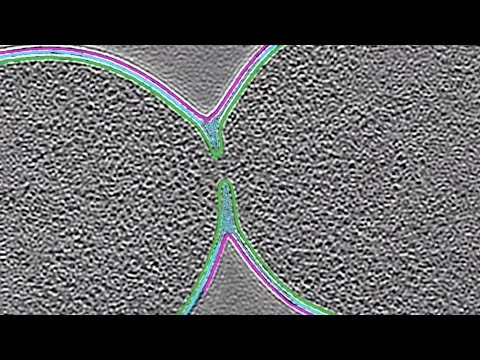
Q. Why is it important for mitochondria to divide?
Mitochondria are not always fusing. They have an equal, balanced activity of division (fission) within most cells. Why do mitochondria divide? Mitochondrial division is important for the remodeling and rearrangement of mitochondrial networks, as well as for enabling mitochondrial segregation during cell division.
Q. What happens to chloroplasts and mitochondria during cell division?
Random segregation. Mitochondria and chloroplasts (and the genes they carry) are randomly distributed to daughter cells during mitosis and meiosis. When the cell divides, the organelles that happen to be on opposite sides of the cleavage furrow or cell plate will end up in different daughter cells 3.
Table of Contents
- Q. Why is it important for mitochondria to divide?
- Q. What happens to chloroplasts and mitochondria during cell division?
- Q. What happens to organelles when cells divide?
- Q. Is mitochondria involved in cell division?
- Q. What is the name of the inner membrane of mitochondria?
- Q. What do the proteins in the mitochondria do?
- Q. What is primary purpose of cristae in the mitochondria?
- Q. How does Mitochondria produce energy for the cell answers?
- Q. How do mitochondria produce energy for the cell?
- Q. How are proteins exported from the cell?
Q. What happens to organelles when cells divide?
The Mitosis Cell Cycle During this time, cells are gathering nutrients and energy. When a cell divides during mitosis, some organelles are divided between the two daughter cells. For example, mitochondria are capable of growing and dividing during the interphase, so the daughter cells each have enough mitochondria.
Q. Is mitochondria involved in cell division?
Mitochondria are organelles with key roles in cellular metabolism. They have unique cellular dynamics to ensure their proper distribution to dividing cells and high fidelity of inheritance of their genome in a maternal mode of transmission.
Q. What is the name of the inner membrane of mitochondria?
cristae
Q. What do the proteins in the mitochondria do?
Mitochondrial proteins are proteins that reside within the mitochondria of cells, including within the cristae of the inner mitochondrial membrane. Mitochondrial proteins are generally involved in mitochondrial function, including carrying out reactions of the electron transport chain.
Q. What is primary purpose of cristae in the mitochondria?
What is the primary purpose of cristae in the mitochondria? Explanation: The importance of the cristae comes from the fact that they greatly increase the surface area of the inner membrane of the mitochondria. This is important because this membrane houses the electron transport chain proteins.
Q. How does Mitochondria produce energy for the cell answers?
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell because they “burn” or break the chemical bonds of glucose to release energy to do work in a cell. This releases energy (ATP) for the cell. The more active a cell (such as a muscle cell), the more mitochondria it will have.
Q. How do mitochondria produce energy for the cell?
Mitochondria, using oxygen available within the cell convert chemical energy from food in the cell to energy in a form usable to the host cell. NADH is then used by enzymes embedded in the mitochondrial inner membrane to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In ATP the energy is stored in the form of chemical bonds.
Q. How are proteins exported from the cell?
Proteins destined to be secreted move through the secretory pathway in the following order: rough ER → ER-to-Golgi transport vesicles → Golgi cisternae → secretory or transport vesicles → cell surface (exocytosis) (see Figure 17-13). Small transport vesicles bud off from the ER and fuse to form the cis-Golgi reticulum.