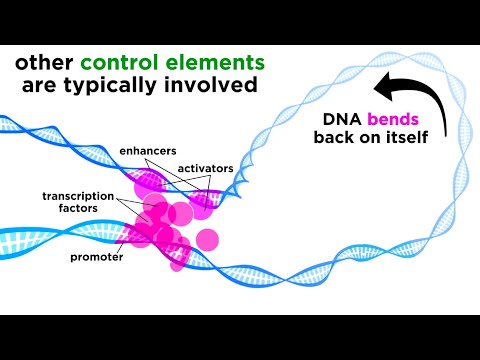
The regulation of gene expression conserves energy and space. It would require a significant amount of energy for an organism to express every gene at all times, so it is more energy efficient to turn on the genes only when they are required.
Q. How can environmental factors affect the expression of genes quizlet?
Environmental factors can affect gene expression such as: the production of skin pigmentation during exposure to sunlight in humans. In embryonic development, the embryo contains an uneven distribution of chemicals called morphogens.
Table of Contents
- Q. How can environmental factors affect the expression of genes quizlet?
- Q. What science studies how environment affects gene expression quizlet?
- Q. What are two functions of gene regulatory proteins?
- Q. What is an outcome of gene expression?
- Q. What is gene expression for dummies?
- Q. How is gene expression measured?
- Q. What are the two stages of gene expression?
- Q. How does diet affect gene expression?
- Q. What blots are used to detect gene expression?
- Q. How do Microarrays measure gene expression?
- Q. Why Western blotting is used?
- Q. Which gel is used in Western blotting?
- Q. What is the difference between SDS PAGE and Western blotting?
- Q. What is the principle of Western blotting?
- Q. Why do Western blots use 2 antibodies?
Q. What science studies how environment affects gene expression quizlet?
What traits are influenced by more than one gene? What science studies how environment affects gene expression? epigenetics. When would monozygotic (identical) twins be produced?
Q. What are two functions of gene regulatory proteins?
Most of the known phosphorylated response regulators employ the two-component system to stimulate or repress the transcription of specific targetted genes. Allosteric regulatory proteins bring about the alteration of metabolic pathways by utilizing end product repression, enzyme induction, and catabolite repression.
Q. What is an outcome of gene expression?
Gene expression is the process by which the instructions in our DNA are converted into a functional product, such as a protein. It acts as both an on/off switch to control when proteins are made and also a volume control that increases or decreases the amount of proteins made.
Q. What is gene expression for dummies?
Gene expression is the process by which the information encoded in a gene is used to direct the assembly of a protein molecule. The cell reads the sequence of the gene in groups of three bases.
Q. How is gene expression measured?
Measurement techniques Gene expression measurement is usually achieved by quantifying levels of the gene product, which is often a protein. However, the gene expression level can also be inferred by measuring the level of mRNA, which is achieved using a technique called Northern blotting.
Q. What are the two stages of gene expression?
Transcription: the production of messenger RNA (mRNA) by the enzyme RNA polymerase, and the processing of the resulting mRNA molecule. Translation: the use of mRNA to direct protein synthesis, and the subsequent post-translational processing of the protein molecule.
Q. How does diet affect gene expression?
Tighter chromatin restricts the expression of genes. When we eat, tiny molecules that are broken down from food including carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and vitamins, are transported throughout the body to be used as energy or as building blocks.
Q. What blots are used to detect gene expression?
The northern blot, or RNA blot, is a technique used in molecular biology research to study gene expression by detection of RNA (or isolated mRNA) in a sample. Northern blotting takes its name from its similarity to the first blotting technique, the Southern blot, named for biologist Edwin Southern.
Q. How do Microarrays measure gene expression?
A microarray is a laboratory tool used to detect the expression of thousands of genes at the same time. The DNA molecules attached to each slide act as probes to detect gene expression, which is also known as the transcriptome or the set of messenger RNA (mRNA) transcripts expressed by a group of genes.
Q. Why Western blotting is used?
A western blot is a laboratory method used to detect specific protein molecules from among a mixture of proteins. Western blots can also be used to evaluate the size of a protein of interest, and to measure the amount of protein expression.
Q. Which gel is used in Western blotting?
agarose gel
Q. What is the difference between SDS PAGE and Western blotting?
SDS-PAGE is an electrophoresis method that separates proteins by mass. Western blot is an analytical technique to identify the presence of a specific protein within a complex mixture of proteins, where gel electrophoresis is usually used as the first step in procedure to separate the protein of interest.
Q. What is the principle of Western blotting?
Western blotting (protein blotting or immunoblotting) is a rapid and sensitive assay for detection and characterization of proteins. It is based on the principle of immunochromatography where proteins are separated into polyacrylamide gel according to their molecular weight.
Q. Why do Western blots use 2 antibodies?
Secondary antibodies are used for the indirect detection of a target to which a specific primary antibody is first bound. The secondary antibody must have specificity both for the antibody species as well as the isotype of the primary antibody being used.