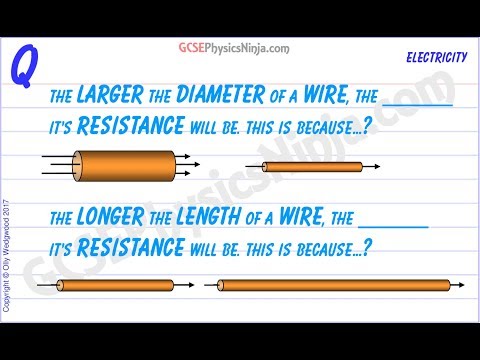
As the length increases, the number of collisions by the moving free electrons with the fixed positive ions increases as more number of fixed positive ions are present in an increased length of the conductor. As a result, resistance increases.
Q. What happen to the current as the resistance increases?
Answer: the current in a given circuit is inversely proportional to the resistance in the circuit, which means that the current will decrease if the resistance is increased.
Table of Contents
- Q. What happen to the current as the resistance increases?
- Q. Is length directly proportional to resistance?
- Q. What happens to the resistance if the length is doubled?
- Q. Is resistance directly proportional to temperature?
- Q. Is the resistance inversely proportional to the temperature?
- Q. Does resistance depend on temperature?
- Q. What is the relation between temperature and resistance?
- Q. What is the relation between resistance and current?
- Q. At which temperature is the resistance higher?
- Q. What happens to resistance when temperature increases?
- Q. What happens to current when temperature increases?
- Q. Which metal resistance decreases with increase in temperature?
- Q. Why resistance decreases with increase in area?
- Q. Why does metal resistance increase with temperature?
- Q. For which of the following resistance decreases as temperature increases?
- Q. For which of the following the resistance decreases?
- Q. Why does the resistance of carbon decreases with temperature?
- Q. In which substance does not resistance decreases with increase in temperature?
- Q. What will happen to the resistance of mica if there is an increase in the temperature?
- Q. Which material is having a small value of temperature coefficient of resistance?
- Q. Why does resistance decrease with temperature in semiconductors?
- Q. Does a semiconductor resistance increase or decrease with temperature?
- Q. How much does resistance change with temperature?
- Q. Does resistivity depend on length?
Q. Is length directly proportional to resistance?
The resistance of a wire is directly proportional to its length and inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area. The resistance of a conductor, or circuit element, generally increases with increasing temperature.
Q. What happens to the resistance if the length is doubled?
What happens to resistance when length is doubled? From the equation, we understand that resistance is directly proportional to the length of the conductor and inversely proportional to the crossectional area of the conductor. Doubling the length doubles the resistance.
Q. Is resistance directly proportional to temperature?
The resistance increases as the temperature of a metallic conductor increase, so the resistance is directly proportional to the temperature.
Q. Is the resistance inversely proportional to the temperature?
Temperature Dependence of Resistivity Resistivity is indirectly proportional to the temperature. In other words, as you increase the temperature of materials, their resistivities will decrease. But this is not true for every material i.e., all materials do not have the same dependence on temperature.
Q. Does resistance depend on temperature?
Since the resistance of some conductor, such as a piece of wire, depends on collisions within the wire itself, the resistance depends on temperature. With increasing temperature, the resistance of the wire increases as collisions within the wire increase and “slow” the flow of current.
Q. What is the relation between temperature and resistance?
As temperature rises, the number of phonons increases and with it the likelihood that the electrons and phonons will collide. Thus when temperature goes up, resistance goes up. For some materials, resistivity is a linear function of temperature. The resistivity of a conductor increases with temperature.
Q. What is the relation between resistance and current?
The relationship between current, voltage and resistance is expressed by Ohm’s Law. This states that the current flowing in a circuit is directly proportional to the applied voltage and inversely proportional to the resistance of the circuit, provided the temperature remains constant.
Q. At which temperature is the resistance higher?
For metallic conductors, resistance is directly proportional to temperature. Thus, resistance is higher at T2
Q. What happens to resistance when temperature increases?
The resistance of a conductor increases with an increase in temperature because the thermal velocity of the free electrons increase as the temperature increases. This results in an increase in the number of collisions between the free electrons.
Q. What happens to current when temperature increases?
Temperature affects how electricity flows through an electrical circuit by changing the speed at which the electrons travel. This is due to an increase in resistance of the circuit that results from an increase in temperature. Likewise, resistance is decreased with decreasing temperatures.
Q. Which metal resistance decreases with increase in temperature?
Answer. the metaliods silicon germanium and semiconductors..and blah blah..are elements resistance decreases on increases temp….
Q. Why resistance decreases with increase in area?
Adding more wires in parallel decreases the resistance of that circuit path. So, bigger cross sectional area = more wires in parallel = lower resistance. And hence the inverse proportionality relation is responsible for increase in area, decrease in resistance property.
Q. Why does metal resistance increase with temperature?
Heating a metal conductor makes it more difficult for electricity to flow through it. These collisions cause resistance and generate heat. Heating the metal conductor causes atoms to vibrate more, which in turn makes it more difficult for the electrons to flow, increasing resistance.
Q. For which of the following resistance decreases as temperature increases?
In insulators and partial conductors such as carbon, increase in temperature results in decrease in resistance. Thus semiconductors or insulators are said to be in negative temperature coefficient of resistance.
Q. For which of the following the resistance decreases?
Q. Why does the resistance of carbon decreases with temperature?
Carbon is a insulator and the temperature coefficient for the insulators is negative. so because Temperature coefficient of resistivity of carbon is negative . Therefore its resistance decreases with increase in temperature.
Q. In which substance does not resistance decreases with increase in temperature?
Complete step-by-step solution Hence, resistivity of constantan does not decrease with increase in temperature. Copper and silver are metals and are good conductors.
Q. What will happen to the resistance of mica if there is an increase in the temperature?
Mica has negative temperature coefficient of resistance. So, resistance will decrease with increase in temperature.
Q. Which material is having a small value of temperature coefficient of resistance?
Nichrome
Q. Why does resistance decrease with temperature in semiconductors?
When the temperature in increased the forbidden gap between the two bands becomes very less and the electrons move from the valence band to the conduction band. Thus when the temperature is increased in a semiconductor, the density of the charge carriers also increases and the resistivity decreases.
Q. Does a semiconductor resistance increase or decrease with temperature?
When temperature is increased in case of a semiconductor the free electron gets more energy to cross the energy gap to the conduction band from the valence band.so now more electrons can go easily to the conduction band so resistance decreases with temperature.
Q. How much does resistance change with temperature?
Thus, resistance generally increases with temperature. For small temperature changes the resistivity varies linearly with temperature: r = ro (1 + a DT), where a is the temperature coefficient of resistivity. which means we’re assuming that length and area don’t change as temperature changes.
Q. Does resistivity depend on length?
The resistivity of a material is the resistance of a wire of that material of unit length and unit cross-sectional area. The resistivity of a material depends on its nature and the temperature of the conductor, but not on its shape and size.