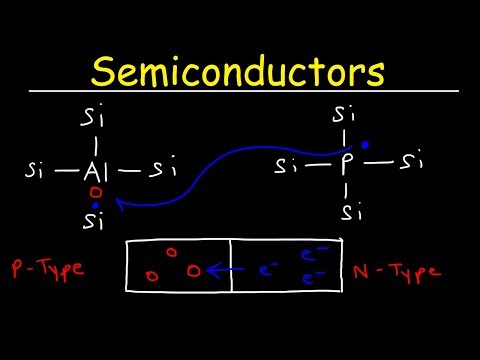
Q. Why P type semiconductor is called acceptor?
Since holes will “accept” free electrons, a Group 3 impurity is also called an acceptor. Because an acceptor donates excess holes, which are considered to be positively charged, a semiconductor that has been doped with an acceptor is called a p-type semiconductor; “p” stands for positive.
Q. What are charge carriers in p type semiconductor?
In p− type semiconductors, holes are the majority carriers and electrons are to minority carriers. Therefore, the charge carrier in a p−type semiconductor are holes in large number and electrons in the smaller number.
Table of Contents
- Q. Why P type semiconductor is called acceptor?
- Q. What are charge carriers in p type semiconductor?
- Q. Why holes are majority carriers in p type semiconductor?
- Q. Why are electron carriers present in P?
- Q. Why is it called P-type?
- Q. How n-type and p-type semiconductors are produced?
- Q. How p-type materials are formed?
- Q. Is P-type negative or positive?
- Q. How do you know if type is N or P?
- Q. How pn junction is formed?
- Q. Why pn junction is called a diode?
- Q. What is application of zener diode?
- Q. Why is PN junction used?
- Q. What is use of PN diode?
- Q. What is breakdown and its types?
- Q. What is done for Zener breakdown?
- Q. What is the cause of reverse breakdown voltage?
- Q. What is the difference between Zener and avalanche breakdown?
- Q. Why zener diode is reverse biased?
- Q. Why zener diode is not used in rectifiers?
Q. Why holes are majority carriers in p type semiconductor?
A p-type impurity is a material in which the atoms have only 3 Valence Electrons. Because of a large existence of P-type material in a p-type semiconductor, it has more holes as compared to free electrons. Hence holes are majority carriers.
Q. Why are electron carriers present in P?
In p type semiconductor, there are excess holes due to trivalent impurity, but some of the electrons in valence band move to conduction band ( due to thermal energy). So there are few electron carriers in p type semiconductor. Similarly there are few holes present in n type semiconductor.
Q. Why is it called P-type?
The term p-type refers to the positive charge of a hole. As opposed to n-type semiconductors, p-type semiconductors have a larger hole concentration than electron concentration. In p-type semiconductors, holes are the majority carriers and electrons are the minority carriers.
Q. How n-type and p-type semiconductors are produced?
Pentavalent impurities Impurity atoms with 5 valence electrons produce n-type semiconductors by contributing extra electrons. Trivalent impurities Impurity atoms with 3 valence electrons produce p-type semiconductors by producing a “hole” or electron deficiency.
Q. How p-type materials are formed?
The extrinsic p-Type Semiconductor is formed when a trivalent impurity is added to a pure semiconductor in a small amount, and as a result, a large number of holes are created in it. A large number of holes are provided in the semiconductor material by the addition of trivalent impurities like Gallium and Indium.
Q. Is P-type negative or positive?
The symbols p and n come from the sign of the charge of the particles: positive for holes and negative for electrons.
Q. How do you know if type is N or P?
If the dopant has more electrons in the outer shell than the semiconductor material, it’s going to be n-type, and with less electrons in the outer shell, it’s p-type.
Q. How pn junction is formed?
P-n junctions are formed by joining n-type and p-type semiconductor materials, as shown below. However, in a p-n junction, when the electrons and holes move to the other side of the junction, they leave behind exposed charges on dopant atom sites, which are fixed in the crystal lattice and are unable to move.
Q. Why pn junction is called a diode?
Diodes. Diodes allow current flow in one direction but not the other. A diode is called a diode because it has two distinct electrodes (i.e. terminals), called the anode and the cathode. A diode is electrically asymmetric because current can flow freely from the anode to the cathode, but not in the other direction.
Q. What is application of zener diode?
Zener diodes are used for voltage regulation, as reference elements, surge suppressors, and in switching applications and clipper circuits. The load voltage equals breakdown voltage VZ of the diode.
Q. Why is PN junction used?
When the diode is forward-biased, it can be used in LED lighting applications. It is used as rectifiers in many electric circuits and as a voltage-controlled oscillator in varactors….Applications of PN Junction Diode.
| Semiconductor Diode | Zener Diode |
|---|---|
| Extrinsic Semiconductors | Electric Field Lines |
Q. What is use of PN diode?
A p-n junction diode is a two terminal device that allows electric current in one direction and blocks electric current in another direction. In forward bias condition, the diode allows electric current whereas in reverse bias condition, the diode does not allow electric current.
Q. What is breakdown and its types?
Different Types Of Break down Diodes mainly includes Signal diode, Zener diode, Tunnel diode, Gunn diode, Crystal diode, Varactor diode, Constant current diode, Light emitting diode, IR leds, Schottky diode, PIN diodes, Avalanche diode, Laser diode, Shockley diode, Photodiodes, Transient Voltage suppression diode.
Q. What is done for Zener breakdown?
Zener breakdown occurs when the electric field near the junction becomes large enough to excite valence electrons directly into the conduction band.
Q. What is the cause of reverse breakdown voltage?
When a PN junction is reversed biased it allows very small current to flow through it. If reverse bias is made too high, the current through PN junction increases abruptly and the voltage at which this phenomenon occurs is called breakdown voltage . At this breakdown voltage , the crystal structure breaks down.
Q. What is the difference between Zener and avalanche breakdown?
The main difference between Zener breakdown and avalanche breakdown is their mechanism of occurrence. Zener breakdown occurs because of the high electric field whereas, the avalanche breakdown occurs because of the collision of free electrons with atoms. Both these breakdowns can occur simultaneously.
Q. Why zener diode is reverse biased?
Zener diodes are simply reverse-biased diodes that can withstand operating in breakdown. As the reverse bias voltage increases, Zener diodes continue to conduct a constant amount of current (the saturation current), until a certain voltage is reached.
Q. Why zener diode is not used in rectifiers?
No, we don’t prefer to use a Zener Diode in a rectifier circuit because for a rectifier circuit a high maximum peak inverse voltage is required. Unlike the normal p-n junction diode, a Zener diode has a low peak inverse voltage. This is an undesirable property for the rectifier circuit.