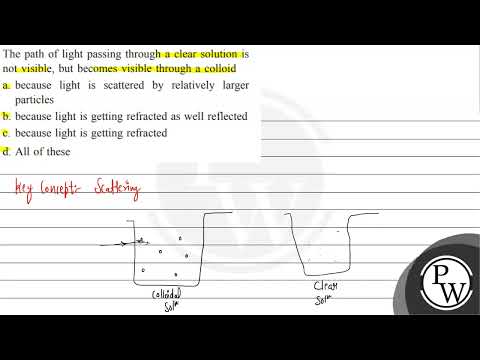
The particles of a solution are smaller than 1 nm (10-9 metre) in diameter. So, they cannot be seen by naked eyes. Because of very small particle size, they do not scatter a beam of light passing through the solution. So, the path of light is not visible in a solution.
Q. How does light travel in a straight line experiment?
Two experiments are used to demonstrate how light travels in straight lines. In the first example, the presenter arranges three pieces of card, with holes in, in an uneven line. The light stops and cannot travel through all three cards. When she arranges the holes in a straight line, the light can travel through.
Table of Contents
- Q. How does light travel in a straight line experiment?
- Q. What is the solution of path of light?
- Q. Which solution or solutions will scatter the path of light passing through it?
- Q. What happens when light passes through colloidal solution?
- Q. Is the path of light in a suspension give reason?
- Q. What is Tyndall effect explain with diagram?
- Q. What is aerosol give example?
- Q. What is aerosol short answer?
- Q. Is moisture in the atmosphere an aerosol?
Q. What is the solution of path of light?
The path of light gets illuminated in a colloidal solution as its particles size are big enough to scatter the light passing through it.
Q. Which solution or solutions will scatter the path of light passing through it?
Colloids are unlike solutions because their dispersed particles are much larger than those of a solution. The dispersed particles of a colloid cannot be separated by filtration, but they scatter light, a phenomenon called the Tyndall effect .
Q. What happens when light passes through colloidal solution?
(i) When a beam of light is passed through a colloidal solution, then light scatter from the particles. This is known as the Tyndall effect. This scattering of light illuminates the path of the beam in the colloidal solution. (iii) The colloidal particles are charged either a positive or negative charge.
Q. Is the path of light in a suspension give reason?
Explanation: When light passes through the suspension it falls over the particles of the solution and colloids with them. This causes a refraction or reflection in their path through certain angles and thus occurs scattering in the light beam. Due to scattering of light, the path of light is illuminated.
Q. What is Tyndall effect explain with diagram?
The Tyndall effect is the phenomenon in which the particles in a colloid scatter the beams of light that are directed at them. Generally, blue light is scattered to a greater extent when compared to red light. This is because the wavelength of blue light is smaller than that of red light.
Q. What is aerosol give example?
What are aerosols? An aerosol is a collection of solid particles or liquid droplets dispersed in air. Examples include smoke, fog, sea spray and pollution particles from vehicles. Particle sizes can range from the nanometre (a millionth of a millimetre) to the millimetre scale.
Q. What is aerosol short answer?
An aerosol (abbreviation of “aero-solution”) is a suspension of fine solid particles or liquid droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be natural or anthropogenic. Examples of natural aerosols are fog or mist, dust, forest exudates and geyser steam.
Q. Is moisture in the atmosphere an aerosol?
The atmosphere is an aerosol with humid air as the dispersion medium and particles as the disper- sed phases.