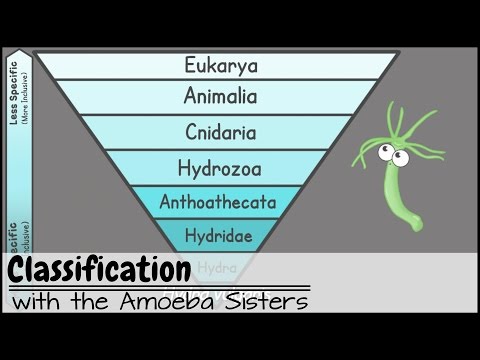
How has the system of classifying organisms changed since Linnaeus’s work? -Levels have been taken away from the hierarchy. -Organisms have been identified simply as plants or animals. More levels have been added to the hierarchy.
Q. Which statement best summarizes how classification systems have changed over time classification systems have become simpler to allow for all the dis?
The answer is the second option or B, “Classification systems have become more complex to allow for all the discoveries made about organisms.” Classification systems were created with the purpose of classifying living things such as plants, animals, species in general.
Table of Contents
- Q. Which statement best summarizes how classification systems have changed over time classification systems have become simpler to allow for all the dis?
- Q. Why has the classification system changed over time?
- Q. Why do classification systems change over time scientists find new evidence in their studies Brainly?
- Q. Which organisms are closely related?
- Q. Which is the best test to show the relatedness of two organisms?
- Q. Which animal is most closely related to humans?
- Q. Which organism has DNA that is least like human DNA?
- Q. What organism has the most DNA?
- Q. Which organism is most different to humans?
- Q. Would you expect a difference between human and onion DNA?
- Q. What is the most complex species on Earth?
- Q. Do humans and trees share genes?
- Q. Do trees have genders?
- Q. What animals have the closest DNA to humans?
- Q. What plant shares the most DNA with humans?
- Q. How much DNA do I share with a banana?
- Q. Does human DNA match a banana?
- Q. How much DNA do humans share with worms?
- Q. Are humans 99 percent chimp?
- Q. What animal do we share 70% DNA with?
- Q. What does a worm want with 20000 genes?
- Q. How do humans have so few genes?
- Q. Why are humans more complex than worms?
- Q. Are humans related to worms?
Q. Why has the classification system changed over time?
Why do classification systems change over time? When scientist find new species that may have to change classification systems in order to accommodate them. DNA sequencing has also let us find out more about evolutionary relationships. This means that scientists have to change the way they classify them.
Q. Why do classification systems change over time scientists find new evidence in their studies Brainly?
Classification system changes because the scientists find new evidence in their studies. Explanation: The world is always changing and growing and dying as well as developing, so over time things change.
Q. Which organisms are closely related?
The example of the closely related organism comes from order Hominidae. This includes the humans, chimpanzees, and gorillas similar features and characteristics and are expected to have originated from the common ancestor.
Q. Which is the best test to show the relatedness of two organisms?
Answer Expert Verified according to some evolusionist you can tell the best relatedness of organism in which they are identical in DNA nucleic acid and as well as their amino acids sequence , their homologous and analogous structure, and some the same in genus and species.
Q. Which animal is most closely related to humans?
chimpanzee
Q. Which organism has DNA that is least like human DNA?
chimpanzees
Q. What organism has the most DNA?
water flea Daphnia
Q. Which organism is most different to humans?
Researchers distinguished DNA of the comb jellyfish as the most distinct from humans’ in a recent study. Sponges are more directly related to humans than the comb jellyfish is. But, unlike the sponge, the comb jelly possesses its own nervous system, according to research by Assistant Professor of Biology Casey Dunn.
Q. Would you expect a difference between human and onion DNA?
Since the onion (Allium cepa) is a diploid organism having a haploid genome size of 15.9 Gb, it has 4.9x as much DNA as does a human genome (3.2 Gb).
Q. What is the most complex species on Earth?
A microscopic, see-through water flea is the most complex creature ever studied, genomically speaking. Daphnia pulex is the first crustacean to ever have its genome sequenced, and it turns out it has about 31,000 genes — 25 percent more than we humans.
Q. Do humans and trees share genes?
Primate Family Tree Due to billions of years of evolution, humans share genes with all living organisms. The percentage of genes or DNA that organisms share records their similarities.
Q. Do trees have genders?
Trees can have either male or female parts. In addition, there are also trees that do not contain any flowers at all, making it even harder to figure out the tree’s gender. Dioecious Trees. If a tree is dioecious it only has male or female parts, not both.
Q. What animals have the closest DNA to humans?
Although figures vary from study to study, it’s currently generally accepted that chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) and their close relatives the bonobos (Pan paniscus) are both humans’ closest-living relatives, with each species sharing around 98.7% of our DNA.
Q. What plant shares the most DNA with humans?
Buzzing right around, bees share about 44 percent of human DNA. We share about 26 percent of our “housekeeping” genes with these single-cell organisms. We share approximately 15 percent of our DNA with this plant.
Q. How much DNA do I share with a banana?
“You share 50 percent of your DNA with each of your parents. But with bananas, we share about 50 percent of our genes, which turns out to be only about 1 percent of our DNA,” emails Mike Francis, a Ph. D. student in bioinformatics at the University of Georgia.
Q. Does human DNA match a banana?
We do in fact share about 50% of our genes with plants – including bananas.” “Bananas have 44.1% of genetic makeup in common with humans.” “Humans share 50% of our DNA with a banana.”
Q. How much DNA do humans share with worms?
(Here’s a clue: We share 21 percent of our DNA with a roundworm).
Q. Are humans 99 percent chimp?
Ever since researchers sequenced the chimp genome in 2005, they have known that humans share about 99% of our DNA with chimpanzees, making them our closest living relatives.
Q. What animal do we share 70% DNA with?
4. It’s probably not that surprising to learn that humans share 98% of our DNA with chimpanzees–but incredibly, we also share 70% with slugs and 50% with bananas.
Q. What does a worm want with 20000 genes?
In summary, the number of known RNA genes is already well over 1,000. These can be added to the 18,000-19,000 predicted protein-coding genes, to give a total of something like 20,000 as a nice round number – hence the title of this article.
Q. How do humans have so few genes?
The old notion of one gene/one protein has gone by the board: It is now clear that many genes can make more than one protein. In the past few years, it has become clear that a phenomenon called alternative splicing is one reason human genomes can produce such complexity with so few genes.
Q. Why are humans more complex than worms?
“Instead, it was the ones that regulate the structure and architecture of the chromatin and how it changes.” Chromatin is everything that forms the chromosomes in our cells—DNA and proteins—which means that the way our genetic material is packaged is what makes us more complex than worms.
Q. Are humans related to worms?
People have more in common with deep-sea worms than one might suspect. Over 500 million years ago, humans and certain worms shared a common ancestor, and people still share thousands of genes with the worms, said scientists who recently sequenced genomes from two marine worm species.