Decreases in demand Conversely, demand can decrease and cause a shift to the left of the demand curve for a number of reasons, including a fall in income, assuming a good is a normal good, a fall in the price of a substitute and a rise in the price of a complement.
Q. What are the five factors that affect demand?
The quantity demanded (qD) is a function of five factors—price, buyer income, the price of related goods, consumer tastes, and any consumer expectations of future supply and price.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the five factors that affect demand?
- Q. What leads to an increase in supply?
- Q. Why does price increase when demand increases?
- Q. Does price increase when demand increases?
- Q. Does price affect demand?
- Q. How does weather affect demand?
- Q. What is law of demand with example?
- Q. Why does price rise when there is a shortage?
- Q. When price go up does supply go up?
Q. What leads to an increase in supply?
As price increases firms have an incentive to supply more because they get extra revenue (income) from selling the goods. If price changes, there is a movement along the supply curve, e.g. a higher price causes a higher amount to be supplied.
Q. Why does price increase when demand increases?
An increase in demand will cause an increase in the equilibrium price and quantity of a good. 1. The increase in demand causes excess demand to develop at the initial price. Excess demand will cause the price to rise, and as price rises producers are willing to sell more, thereby increasing output.
Q. Does price increase when demand increases?
When demand exceeds supply, prices tend to rise. There is an inverse relationship between the supply and prices of goods and services when demand is unchanged. However, when demand increases and supply remains the same, the higher demand leads to a higher equilibrium price and vice versa.
Q. Does price affect demand?
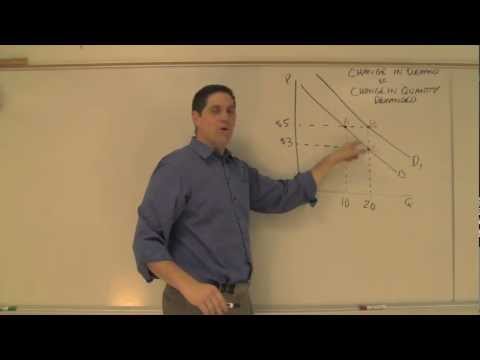
A change in the price of a good or service causes a movement along a specific demand curve, and it typically leads to some change in the quantity demanded, but it does not shift the demand curve.
Q. How does weather affect demand?
As well as affecting our mood, our propensity to spend, and our preferred channels of purchase, weather is a critical driver of product demand. Likewise, a 1 degree F drop in temperature in the US can lead to a huge increase in sales of soup, porridge, and lip-care products.
Q. What is law of demand with example?
Movies. If movie ticket prices declined to $3 each, for example, demand for movies would likely rise. As long as the utility from going to the movies exceeds the $3 price, demand will rise. As soon as consumers are satisfied that they’ve seen enough movies, for the time being, demand for tickets will fall.
Q. Why does price rise when there is a shortage?
Therefore, shortage drives price up. If a surplus exist, price must fall in order to entice additional quantity demanded and reduce quantity supplied until the surplus is eliminated. If a shortage exists, price must rise in order to entice additional supply and reduce quantity demanded until the shortage is eliminated.
Q. When price go up does supply go up?
If the supply increases, the price decreases, and if the supply decreases, the price increases. This is called an indirect relationship, where if one variable goes up, the other variable goes down.