A philosophical, logical discussion using questions and answers on ethics or social problems is an example of dialectic. The contradiction between two conflicting forces viewed as the determining factor in their continuing interaction.
Q. What is meant by hegelianism?
: the philosophy of Hegel that places ultimate reality in ideas rather than in things and that uses dialectic to comprehend an absolute idea behind phenomena.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is meant by hegelianism?
- Q. What does dialectic mean?
- Q. What is Hegel known for?
- Q. What are the 3 basic laws of dialectics?
- Q. Does Hegel believe in God?
- Q. Was Kant an atheist?
- Q. What is freedom according to Hegel?
- Q. What does Hegel mean by right?
- Q. What is Hegel’s philosophy of history?
- Q. What is concrete freedom?
- Q. What is state according to Hegel?
- Q. What are Hegel’s views about freedom of the individual?
- Q. Who wrote that the state is perfected rationality?
- Q. Who advocated the pluralistic view of sovereignty?
- Q. Is Hegel an Enlightenment thinker?
- Q. What is Hegel’s earliest form of organization?
- Q. Did Hegel believe free will?
- Q. What did Hegel say was free?
- Q. Is Hegel a determinist?
- Q. Is Hegel still relevant?
- Q. Was Hegel a dualist?
- Q. What is reasonable is real that which is real is reasonable?
- Q. What is Hegel’s absolute spirit?
- Q. What is absolute spirit?
- Q. What does Hegelian dialectic mean?
- Q. What does Hegel mean by Geist?
- Q. What does Geist mean in English?
- Q. What nationality is the name Geist?
Q. What does dialectic mean?
1 philosophy : logic sense 1a(1) 2 philosophy. a : discussion and reasoning by dialogue as a method of intellectual investigation specifically : the Socratic techniques of exposing false beliefs and eliciting truth.
Q. What is Hegel known for?
Hegel’s major works included the Phenomenology of Spirit (1807; also called the Phenomenology of Mind); the Science of Logic, in two parts (1812 and 1816); Encyclopedia of the Philosophical Sciences (1817); the Philosophy of Right (1821); and posthumously published lectures on aesthetics, the philosophy of religion.
Q. What are the 3 basic laws of dialectics?
A reader asks, whether I know the origins of Engel’s so called “three laws of Dialectics”: quantity changes to quality, opposites interpenetrate, and negation of negation. I will first answer about possible sources of these laws in Hegel’s logic and then criticize them as not satisfying.
Q. Does Hegel believe in God?
For Hegel, thought is not philosophical if it is not also religious. Although Hegel stated that God is absolute Spirit and Christianity is the absolute religion, the compatibility of Hegel’s doctrine of God with Christian theology has been a matter of continuing and closely argued debate.
Q. Was Kant an atheist?
In fact, given Kant’s philosophical views on the existence of God as defended throughout his entire mature oeuvre and lectures, Kant himself is a ‘sceptical atheist’ from the standpoint of theoretical reason, i.e., one who stays unconvinced by the theoretical arguments for God’s existence, but who is open to positing …
Q. What is freedom according to Hegel?
The concept of freedom is one which Hegel thought of very great importance; indeed, he believed that it is the central concept in human history. ‘Mind is free’, he wrote, ‘and to actualise this, its essence – to achieve this excellence – is the endeavour of the worldmind in world-history’ (VG, p. 73).
Q. What does Hegel mean by right?
state governed by law Hegel means one. that extends the right of recognition. (Anerkennung) or respect to every one of. its members.
Q. What is Hegel’s philosophy of history?
Hegel regards history as an intelligible process moving towards a specific condition—the realization of human freedom. And he views it to be a central task for philosophy to comprehend its place in the unfolding of history. “History is the process whereby the spirit discovers itself and its own concept” (1857: 62).
Q. What is concrete freedom?
But concrete freedom consists in this, that personal individuality and its particular interests not only achieve their complete development and gain explicit recognition for their right (as they do in the sphere of the family and civil society) but, for one thing, they also pass over of their own accord into the …
Q. What is state according to Hegel?
To Hegel, the state was the culmination of moral action, where freedom of choice had led to the unity of the rational will, and all parts of society were nourished within the health of the whole. However, Hegel remained enchanted with the power of national aspiration.
Q. What are Hegel’s views about freedom of the individual?
Thus, one aspect of Hegel s philosophy which is of greatest significance is the exaltation of the state and complete negation of the individual’s, rights and freedoms. Real freedom of the individual can be realised only in the state. The only way for the individual to be free is to willingly obey the laws of the state.
Q. Who wrote that the state is perfected rationality?
Hegel
Q. Who advocated the pluralistic view of sovereignty?
Harold J. Laski
Q. Is Hegel an Enlightenment thinker?
Hegel turns both the Enlightenment conception of Reason and its religious opposite inside-out. Hegel’s Reason is identified with divine wisdom. It does not merely exist passively in human history, but expresses itself as ‘purposive activity’ in the course of that history.
Q. What is Hegel’s earliest form of organization?
THE Jenenser system, as it is called, is Hegel’s first complete system, consisting of a logic, a metaphysic, philosophy of nature, and philosophy of mind. Hegel formulated it in his lectures at the University of Jena from 1802 to 1806.
Q. Did Hegel believe free will?
Hegel’s analysis of will in PR is one of the most difficult passages in all of Hegel. It is certainly clear that he does not hold to any doctrine of ‘free will’ in the libertarian sense. Like everything in Hegel, the will itself in his view must be conceived as a “unity” or a sublation of these two moments (§7).
Q. What did Hegel say was free?
Hegel likes to say, the path of God in the world. ‘ one’s true being, but to enter into it. He who becomes one with a reasonable society in all its ramifications, becomes, also, one with the divine; and such a man is free.
Q. Is Hegel a determinist?
Hegel eil determinismo Hegel’s concern for determinism induced some scholars to interpret his practical philosophy as a form of determinism or as a form of compatibilism.
Q. Is Hegel still relevant?
Hegel remains important. Hegel’s whole philosophical system was designed to show modern individuals what it actually means to be “Rational”. As long as postmodernist relativism persists, it remains important to understand Hegel’s novel defense of modern reason.
Q. Was Hegel a dualist?
On the other hand, he tried to establish an inclusive philosophy devoid of the deficiencies of previous systems. This duality was the main deficiency of those systems- what Hegel tried to cope with. So, he considered dualism as the source of need to philosophy.
Q. What is reasonable is real that which is real is reasonable?
What is reasonable is real; that which is real is reasonable. Variant translation: What is rational is real; And what is real is rational. Upon this conviction stand not philosophy only but even every unsophisticated consciousness.
Q. What is Hegel’s absolute spirit?
Kant. Hegel has presented an Absolute Spirit which is a unified actuality; unifying nature, man’s civil institutions, art, religion, philosophy and purposiveness of history. Hegel is the extreme opposite. He reverses this and has reason do all the work.
Q. What is absolute spirit?
Spirit is absolute when its self-development has taken on – i.e., has successively confronted and overcome – the complete series of all possible limitations and negations, finally assimilating them as constitutive of its own reality, activity, and self-cognition.
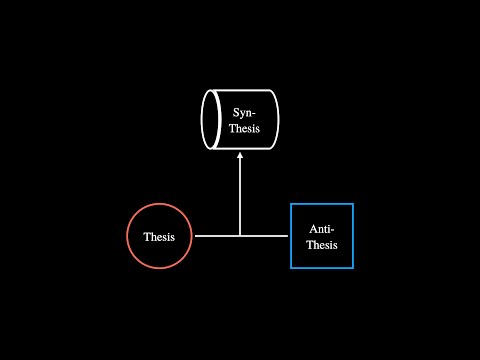
Q. What does Hegelian dialectic mean?
Hegelian dialectic in British English (hɪˈɡeɪlɪan, heɪˈɡiː-) philosophy. an interpretive method in which the contradiction between a proposition (thesis) and its antithesis is resolved at a higher level of truth (synthesis)
Q. What does Hegel mean by Geist?
(6) Hegel holds that the Geist, or mind, essentially instantiates the characteristic threefold structure of consciousness that several of his predecessors (in particular, Kant, Reinhold, and Fichte) had already identified: a structure that both includes and distinguishes from each other consciousness of an object, self …
Q. What does Geist mean in English?
ghost, spirit, mind, intellect
Q. What nationality is the name Geist?
German