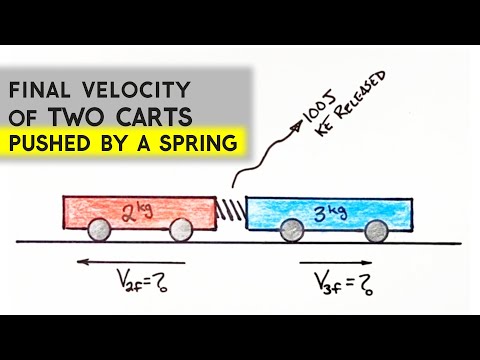
2 Answers. For a perfectly elastic collision, the final velocities of the carts will each be 1/2 the velocity of the initial velocity of the moving cart. For a perfectly inelastic collision, the final velocity of the cart system will be 1/2 the initial velocity of the moving cart.
Q. What do you notice about the velocity of the cart?
The velocity(v) of the cart is its speed and direction. changes A change in velocity is called acceleration (a).
Table of Contents
- Q. What do you notice about the velocity of the cart?
- Q. What will the motion of the cart be like when there is no force at all?
- Q. What will the motion of the cart be like?
- Q. What law of motion is pushing a cart?
- Q. What happens if you push a shopping cart?
- Q. Why is it easier to push an empty cart than a cart full of grocery?
- Q. Which cart is harder to push?
- Q. Why do objects slow down when there is nothing pushing them?
- Q. What 3 things can a force do to an object?
- Q. What are the examples of unbalanced force?
- Q. What are the 5 forces science?
Q. What will the motion of the cart be like when there is no force at all?
1. Form hypothesis: What will the motion of the cart be like when there is no force at all? (There is no friction in this model.) If there is no force the cart will not move and it will stay in its original position. The cart will have the same velocity because there is no friction to slow down the cart.
Q. What will the motion of the cart be like?
Answer: Explanation: the cart motion will be backward motion for there is no action force generated via friction force which acts on the ground harness of the horse.
Q. What law of motion is pushing a cart?
If a person pushes two carts, one empty and one full of groceries, with the same force, the empty cart will travel farther and accelerate more compared to the full cart. This can be used as a real life example of Newton’s second law of motion.
Q. What happens if you push a shopping cart?
When you pull on a wagon, you’re applying a force to that wagon. When you push a shopping cart in the grocery store, you’re applying a force to that shopping cart. The property of an object to stay in constant motion is called inertia, and mass is a measure of that inertia.
Q. Why is it easier to push an empty cart than a cart full of grocery?
An empty grocery cart is easier to move because there is less mass in an empty cart compared to a full cart. Newton’s second law state that an object’s acceleration depends on the mass of the object and the force applied. Something with more mass will need a greater force to move it than something with less mass.
Q. Which cart is harder to push?
Q. Why do objects slow down when there is nothing pushing them?
Draw conclusion: What causes objects to slow down when they are no longer pushed? The reason why the objects started to slow down when they were no longer pushed was because there was friction acting on the wheels, causing the object to slow down and eventuallystop.
Q. What 3 things can a force do to an object?
A force can do one of four things to an object:
- Make it speed up – accelerate.
- Make it slow down – decelerate.
- Change its direction.
- Change its shape.
Q. What are the examples of unbalanced force?
Practically anything that moves is a result of the exertion of unbalanced forces on it. If you kick a football and it moves from one place to another, it means that unbalanced forces are acting upon it. Ball moves from one place to another after kicking it. This is an example of unbalanced force.
Q. What are the 5 forces science?
They are in no particular order gravity, electromagnetism, the weak nuclear force and the strong nuclear force.