1
Q. What are the three laws of gases?
The gas laws consist of three primary laws: Charles’ Law, Boyle’s Law and Avogadro’s Law (all of which will later combine into the General Gas Equation and Ideal Gas Law).
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the three laws of gases?
- Q. What is r in PV NRT?
- Q. What is the value of Z at high pressure?
- Q. What is the value for the perfect gas?
- Q. What if compressibility factor is less than 1?
- Q. When z1 gas is less compressible?
- Q. What happens when Z 1?
- Q. How does Z calculate compressibility factor?
- Q. What is compressibility factor Z?
- Q. What is meant by compressibility?
- Q. What is critical compressibility factor?
- Q. How does compressibility factor vary with pressure?
- Q. Why do real gases deviate from ideal Behaviour?
Q. What is r in PV NRT?
PV = nRT. The factor “R” in the ideal gas law equation is known as the “gas constant”. R = PV. nT. The pressure times the volume of a gas divided by the number of moles and temperature of the gas is always equal to a constant number.
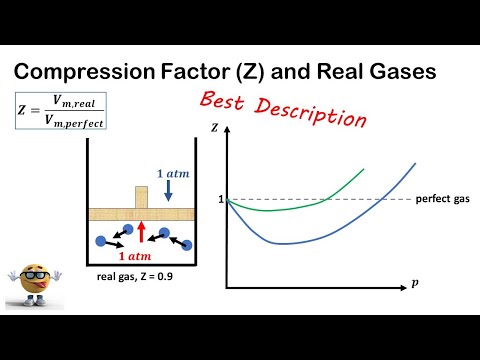
Q. What is the value of Z at high pressure?
Value of Compressibility Factor (z)at low pressure and high pressure(JEE Mains 2014) Q. & A. at low pressure Z= 1- a/VRT for 1 mole gas. at high pressure z= 1+ PB/RT for 1 mole gas.
Q. What is the value for the perfect gas?
8.314472 joules
Q. What if compressibility factor is less than 1?
Is the compressibility factor smaller or greater than 1 at low temperature and high pressure? The compressibility factor of a gas is defined as Z=pV/(nRT). If attractive intermolecular forces dominate then Z tends to be smaller than 1, and vice versa if repulsive forces dominate.
Q. When z1 gas is less compressible?
At Z>1, PV>nRT for real gases. As pressure increases the value of PV increases and gas becomes less compressible. Repulsive forces dominate at this condition.
Q. What happens when Z 1?
Z <1, PV < nRT, it refers to negative deviation i.e. the gas is more compressable than expected from ideal behaviour. The value of Z will be greater than 1(Z>1), shows positive deviation above Boyle’s temperature.
Q. How does Z calculate compressibility factor?
Compressibility factor, usually defined as Z = pV/RT, is unity for an ideal gas.
Q. What is compressibility factor Z?
The compressibility factor Z is defined as the ratio of the actual volume to the volume predicted by the ideal gas law at a given temperature and pressure. Z = (Actual volume) / (volume predicted by the ideal gas law)
Q. What is meant by compressibility?
Compressibility can be defined as the proportional reduction in the thickness of a material under prescribed conditions of increased pressure or compressive loading.37.
Q. What is critical compressibility factor?
The critical compressibility factor Zc defined by. Zc=Pc Vc/NkBTc. (1·1) (Pc: critical pressure, Vc: critical volume, Tc: critical temperature, kB: Boltzmann’s. constant, N: number of molecules) is an important quantity*) which characterizes the property of gas-liquid critical point.
Q. How does compressibility factor vary with pressure?
A graph of the compressibility factor (Z) vs. pressure shows that gases can exhibit significant deviations from the behavior predicted by the ideal gas law. Raising the pressure of a gas increases the fraction of its volume that is occupied by the gas molecules and makes the gas less compressible.
Q. Why do real gases deviate from ideal Behaviour?
Gases deviate from the ideal gas behaviour because their molecules have forces of attraction between them. At high pressure the molecules of gases are very close to each other so the molecular interactions start operating and these molecules do not strike the walls of the container with full impact.