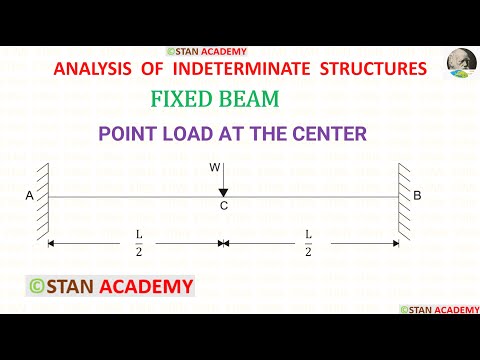
8. What will be the difference in moment acting at both the ends? Explanation: Both ends are not rotating.
Q. What are the example of sinking?
Examples of Sinking and Floating Objects An iron nail sinks in water while a flat cup floats. This is because the nail is unable to displace the amount of water equivalent to its weight. Similarly, an empty plastic bottle floats on water. However, when you fill it up with water, the bottle sinks.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the example of sinking?
- Q. What is sinking of support explain with example?
- Q. What is the degree of indeterminacy of a fixed supported portal frames *?
- Q. What is the degree of indeterminacy of a fixed arch?
- Q. What is degree of statically indeterminacy explain?
- Q. How do we check the Determinacy of a structure?
- Q. What is degree of kinematic indeterminacy?
- Q. What is the degree of redundancy?
- Q. What is indeterminacy structure?
Q. What is sinking of support explain with example?
Answer: Sinking can happen with determinate beams as well. If the sinking of the support is such that it causes the beam to rotate clockwise as a whole, then the resulting moment generated due to sinking is anti-clockwise; and vice versa.
Q. What is the degree of indeterminacy of a fixed supported portal frames *?
What is the degree of indeterminacy of a pin supported portal frame? Explanation: It has 4 unknowns and as usual 3 equilibrium equations. 4.
Q. What is the degree of indeterminacy of a fixed arch?
3 degrees
Q. What is degree of statically indeterminacy explain?
The DEGREE OF STATIC INDETERMINACY (DSI) is the number of redundant forces in the structure. Therefore, the degree of static indeterminacy (DSI) represents the difference between the number of static unknowns (reactions and internal forces) and the number of static equations (equilibrium equations).
Q. How do we check the Determinacy of a structure?
3m+r=20 and 3j+ec=20, so this structure is internally statically determinate (or “S.D.”). e) External Determinacy: r=7,ec=2….Degree of kinematic indeterminacy is given by:
- Dk = 3j – re ……….
- Dk = 3j – re – m ……….
- Dk = 3(j + j’) – re – m + rr ……
- Dk = 6(j + j’) – re – m + rr …..
- Dk = 2(j + j’) – re – m + rr …..
Q. What is degree of kinematic indeterminacy?
The degree of kinematic indeterminacy (DKI) is the minimum number of movements (degrees of freedom, DOF) with which the kinematic configuration of the overall structure can be defined, that is, the number of unknown independent movements of the structure.
Q. What is the degree of redundancy?
The degree of indeterminacy or redundancy is given by the number of extra or redundant reactions to be determined. If a portal frame has more than three reactions it is statically indeterminate, the degree of indeterminacy or redundancy being equal to the number of redundant or extra reactions to be determined.
Q. What is indeterminacy structure?
The indeterminacy in a structure may be external, internal or both. A structure is said to be externally indeterminate if the number of reactions exceeds the number of equilibrium equations. Beams shown in Fig. 1.8(a) and (b) have four reaction components, whereas we have only 3 equations of equilibrium.