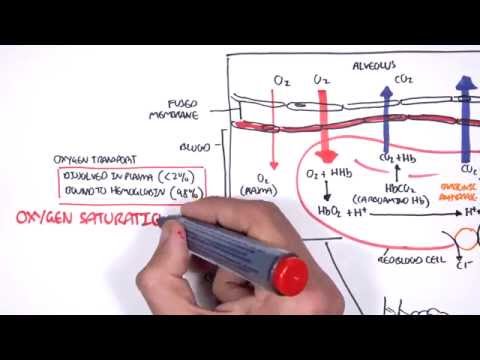
The function of the respiratory system is to move two gases: oxygen and carbon dioxide. Gas exchange takes place in the millions of alveoli in the lungs and the capillaries that envelop them.
Q. Why is respiratory physiology important?
Understanding respiratory physiology can aid the practitioner in diagnosing the cause of respiratory symptoms. The main goals of respiration are oxygen uptake and elimination of carbon dioxide. Secondary goals include acid-base buffering, hormonal regulation, and host defense.
Table of Contents
- Q. Why is respiratory physiology important?
- Q. Why the movement of gases is important to respiratory physiology?
- Q. Why is gas exchange important for the body?
- Q. What are the factors affecting gas exchange?
- Q. How does temperature affect gas exchange?
- Q. What are the features of gas exchange surfaces?
- Q. How does Proning improve gas exchange?
- Q. What factors affect gas exchange in the lungs?
- Q. How is gas exchange measured in the lungs?
- Q. Where in the lungs does gas exchange occur?
- Q. What important activity takes place in the lungs?
- Q. What is the correct pathway of oxygen to the lungs?
- Q. What is the pathway of oxygen through the body?
- Q. How will you describe in your own words the sequence of oxygen carbon dioxide and blood flow?
- Q. How does the respiratory system provide oxygen to the body step by step?
Q. Why the movement of gases is important to respiratory physiology?
Gas exchange is the process by which oxygen and carbon dioxide move between the bloodstream and the lungs. This is the primary function of the respiratory system and is essential for ensuring a constant supply of oxygen to tissues, as well as removing carbon dioxide to prevent its accumulation.
Q. Why is gas exchange important for the body?
Gas exchange is important because it provides oxygen to the cells of living organisms so that they can obtain energy from organic molecules.
Q. What are the factors affecting gas exchange?
There are three main factors that affect gas exchange in both animals and plants:
- Surface area of the membrane. The larger the surface area of the membrane the higher the rate of gas exchange that takes place.
- Concentration gradient.
- Thickness of the membrane.
- The distance of diffusion.
Q. How does temperature affect gas exchange?
As it turns out, temperature affects the affinity, or binding strength, of hemoglobin for oxygen. Specifically, increased temperature decreases the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen. As oxyhemoglobin is exposed to higher temperatures in the metabolizing tissues, affinity decreases and hemoglobin unloads oxygen.
Q. What are the features of gas exchange surfaces?
List the features of gas exchange surfaces in animals.
- They are moist to prevent the cells from drying and to allow gases to dissolve;
- They have a large surface area , so that a lot of gas can diffuse across at the same time;
- They have a high concentration gradient – maintained by the movement of air & blood.
Q. How does Proning improve gas exchange?
In ARDS, an imbalance between blood and air flow develops, leading to poor gas exchange. Prone positioning redistributes blood and air flow more evenly, reducing this imbalance and improving gas exchange.
Q. What factors affect gas exchange in the lungs?
Exercise, smoking, and asthma affect gas exchange: Exercise increases lung volume, respiration rate (breaths per minute), and heart rate. Smoking damages the alveoli, decreases surface area available for gas exchange, and leads to heart disease and lung cancer, a disease that results from an overgrowth of lung tissue.
Q. How is gas exchange measured in the lungs?
DLCO is measured by sampling end-expiratory gas for carbon monoxide (CO) after patients inspire a small amount of carbon monoxide, hold their breath, and exhale. Measured DLCO should be adjusted for alveolar volume (which is estimated from dilution of helium) and the patient’s hematocrit.
Q. Where in the lungs does gas exchange occur?
ALVEOLI are the very small air sacs where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place. CAPILLARIES are blood vessels in the walls of the alveoli.
Q. What important activity takes place in the lungs?
The main function of the lungs is the process of gas exchange called respiration (or breathing). In respiration, oxygen from incoming air enters the blood, and carbon dioxide, a waste gas from the metabolism, leaves the blood.
Q. What is the correct pathway of oxygen to the lungs?
Respiratory System: Pathway of air: nasal cavities (or oral cavity) > pharynx > trachea > primary bronchi (right & left) > secondary bronchi > tertiary bronchi > bronchioles > alveoli (site of gas exchange)
Q. What is the pathway of oxygen through the body?
Inside the air sacs, oxygen moves across paper-thin walls to tiny blood vessels called capillaries and into your blood. A protein called haemoglobin in the red blood cells then carries the oxygen around your body.
Q. How will you describe in your own words the sequence of oxygen carbon dioxide and blood flow?
Answer Expert Verified The inhaled oxygen enters the lungs then oxygen reaches the alveoli. The inhaled oxygen passes quickly through the air-blood barrier going into the blood in the capillaries while carbon dioxide passes quickly from the blood going into the alveoli and then exhaled.
Q. How does the respiratory system provide oxygen to the body step by step?
The respiratory system works directly with the circulatory system to provide oxygen to the body. Oxygen taken in from the respiratory system moves into blood vessels that then circulate oxygen-rich blood to tissues and cells.